Low-temperature operating ZnO-based NO2 sensors: a review
- PMID: 35515369
- PMCID: PMC9057570
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra07328h
Low-temperature operating ZnO-based NO2 sensors: a review
Abstract
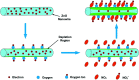
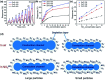
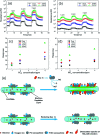
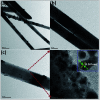
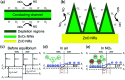
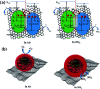
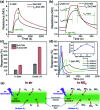
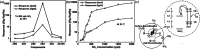
Owing to its excellent physical and chemical properties, ZnO has been considered to be a promising material for development of NO2 sensors with high sensitivity, and fast response and recovery. However, due to the low activity of ZnO at low temperature, most of the current work is focused on detecting NO2 at high operating temperatures (200-500 °C), which will inevitably increase energy consumption and shorten the lifetime of sensors. In order to overcome these problems and improve the practicality of ZnO-based NO2 sensors, it is necessary to systematically understand the effective strategies and mechanisms of low-temperature NO2 detection of ZnO sensors. This paper reviews the latest research progress of low-temperature ZnO nanomaterial-based NO2 gas sensors. Several efficient strategies to achieve low-temperature NO2 detection (such as morphology modification, noble metal decoration, additive doping, heterostructure sensitization, two-dimensional material composites, and light activation) and corresponding sensing mechanisms (such as depletion layer theory, grain boundary barrier theory, spill-over effects) are also introduced. Finally, the challenges and future development directions of low-temperature ZnO-based NO2 sensors are outlined.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
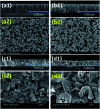
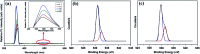
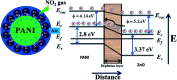
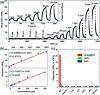
Similar articles
-
Controllable Synthesis of Sheet-Flower ZnO for Low Temperature NO2 Sensor.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Apr 19;13(8):1413. doi: 10.3390/nano13081413. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37110998 Free PMC article.
-
Visible Light-Activated Room Temperature NO2 Gas Sensing Based on the In2O3@ZnO Heterostructure with a Hollow Microtube Structure.ACS Sens. 2024 Jul 26;9(7):3741-3753. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c00919. Epub 2024 Jul 12. ACS Sens. 2024. PMID: 38996081
-
The MoS2/ZnO p-n heterostructure arrays for ultrasensitive ppb-level self-supporting NO2 gas sensors under UV irradiation.Talanta. 2025 Nov 1;294:128194. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2025.128194. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Talanta. 2025. PMID: 40280077
-
Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for NO2 Gas-Sensor Applications: A Review.Nanomicro Lett. 2015;7(2):97-120. doi: 10.1007/s40820-014-0023-3. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Nanomicro Lett. 2015. PMID: 30464961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in ZnO-Based Carbon Monoxide Sensors: Role of Doping.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jun 28;21(13):4425. doi: 10.3390/s21134425. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203318 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Growth Mechanisms of ZnO Micro-Nanomorphologies and Their Role in Enhancing Gas Sensing Properties.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 13;21(4):1331. doi: 10.3390/s21041331. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668546 Free PMC article.
-
Dysprosium Doped Zinc Oxide for NO2 Gas Sensing.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 10;22(14):5173. doi: 10.3390/s22145173. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890853 Free PMC article.
-
High-Performance Room-Temperature NO2 Gas Sensor Based on Au-Loaded SnO2 Nanowires under UV Light Activation.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;12(22):4062. doi: 10.3390/nano12224062. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432348 Free PMC article.
-
Hollow ZnO nanorices prepared by a simple hydrothermal method for NO2 and SO2 gas sensors.RSC Adv. 2021 Oct 13;11(53):33613-33625. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05912b. eCollection 2021 Oct 8. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35497546 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the ordered assembly morphologies of diblock copolymers on the same substrate.RSC Adv. 2022 Oct 5;12(44):28376-28387. doi: 10.1039/d2ra04803e. eCollection 2022 Oct 4. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36320541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen X. Shen Y. Zhang W. Zhang J. Wei D. Lu R. Zhu L. Li H. Shen Y. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018;435:1096–1104. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.222. - DOI
-
- Chen R. Wang J. Xia Y. Xiang L. Sens. Actuators, B. 2018;255:2538–2545. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.059. - DOI
-
- Özgür Ü. Alivov Y. I. Liu C. Teke A. Reshchikov M. A. Doğan S. Cho S.-J. Morkoç H. J. Appl. Phys. 2005;98:041301. doi: 10.1063/1.1992666. - DOI
-
- Li Y. Wang S. Hao P. Tian J. Cui H. Wang X. Sens. Actuators, B. 2018;273:751–759. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.06.110. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

