C-Dot TiO2 nanorod composite for enhanced quantum efficiency under direct sunlight
- PMID: 35515458
- PMCID: PMC9054048
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra03157g
C-Dot TiO2 nanorod composite for enhanced quantum efficiency under direct sunlight
Abstract
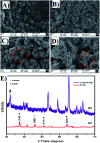
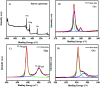
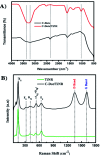
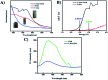
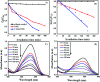
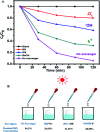
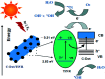
C-Dots obtained from a sustainable route (melon-rinds were used as the source) were combined with TiNRs to create a composite via a simple hydrothermal technique. The obtained materials were subjected to analyses viz. FESEM, XRD, Raman spectroscopy, XPS, PL, FTIR and UV-vis-DRS for understanding their intrinsic nature. The solar photocatalytic performance was evaluated by the degradation of methyl orange (MO) as a model pollutant. The optical properties indicated that there was a clear redshift in the composite with a band gap of 2.49 eV, while the XRD results corresponded to a calculated crystalline size of 24.80 nm. The PL analysis proved the role of C-dots as an electron surge to the TiNRs. The photocatalytic reaction was faster with C-dots as compared to the solo TiNR with a higher degradation of 93.3% within 150 min obeying pseudo-first order kinetics with a rate constant k = 0.01723 min-1. The charge carrier scavenging investigation showed the role of numerous reactive oxygen species (ROS) on the degradation of MO. The formulated composite has demonstrated its ability in effectively handling the contaminants in water. Thus, this study establishes the two-step thermal method as an easy, facile, environmentally-friendly, and low-cost synthesis method for the large-scale production of a photocatalyst.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Green and environmentally sustainable fabrication of SnS2 quantum dots/chitosan nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic performance: Effect of process variables, and water matrices.J Hazard Mater. 2023 Feb 15;444(Pt A):130301. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130301. Epub 2022 Nov 2. J Hazard Mater. 2023. PMID: 36403450
-
Facile synthesis of few-layer MoS2 in MgAl-LDH layers for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity.RSC Adv. 2019 Aug 5;9(42):24280-24290. doi: 10.1039/c9ra03858b. eCollection 2019 Aug 2. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35527890 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of the hybridization between boron-doped carbon quantum dots and n/n-type g-C3N4 homojunction for boosted visible-light photocatalytic activity.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jun;29(27):41272-41292. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-18253-0. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35088270
-
Solar light-driven photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of beta blockers propranolol and atenolol by carbon dot/TiO2 composite.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Mar;29(11):15614-15630. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16796-w. Epub 2021 Oct 10. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34628578
-
Nanostructured TiO2 Sensitized with MoS2 Nanoflowers for Enhanced Photodegradation Efficiency toward Methyl Orange.ACS Omega. 2021 Jun 23;6(26):17071-17085. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02194. eCollection 2021 Jul 6. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34250364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adnan M. A. M. Julkapli N. M. Amir M. N. I. Maamor A. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019;16:547–566. doi: 10.1007/s13762-018-1857-x. - DOI
-
- Curtina J. McInerney C. Gallachóir B. O. Hickey C. Deane P. Deeney P. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2019;116:109402. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.109402. - DOI
-
- Shi L. Shi Y. Zhuo S. Zhang C. Aldrees Y. Aleid S. Wang P. Nano Energy. 2019;60:222–230. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.03.039. - DOI
-
- Kumar S. Nehra M. Deep A. Kedia D. Dilbaghi N. Kim K. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2017;73:821–839. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.172. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

