Recent progress in chemosensors based on pyrazole derivatives
- PMID: 35515469
- PMCID: PMC9054117
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra02394a
Recent progress in chemosensors based on pyrazole derivatives
Abstract
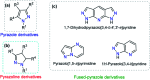
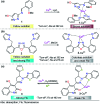
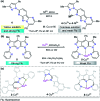
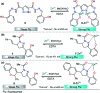
Colorimetric and fluorescent probes based on small organic molecules have become important tools in modern biology because they provide dynamic information concerning the localization and quantity of the molecules and ions of interest without the need for genetic engineering of the sample. In the past five years, these probes for ions and molecules have attracted great attention because of their biological, environmental and industrial significance combined with the simplicity and high sensitivity of absorption and fluorescence techniques. Moreover, pyrazole derivatives display a number of remarkable photophysical properties and wide synthetic versatility superior to those of other broadly used scaffolds. This review provides an overview of the recent (2016-2020) findings on chemosensors containing pyrazole derivatives (pyrazoles, pyrazolines and fused pyrazoles). The discussion focuses on the design and physicochemical properties of chemosensors in order to realize their full potential for practical applications in environmental and biological monitoring (sensing of metal ions, anions, explosives, and biomolecules). We also present our conclusions and outlook for the future.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures









References
-
- Malik L. A. Bashir A. Qureashi A. Pandith A. H. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019;17:1495–1521. doi: 10.1007/s10311-019-00891-z. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

