The tetrameric peptide LfcinB (20-25)4 derived from bovine lactoferricin induces apoptosis in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line
- PMID: 35515557
- PMCID: PMC9065741
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04145a
The tetrameric peptide LfcinB (20-25)4 derived from bovine lactoferricin induces apoptosis in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line
Abstract
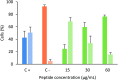
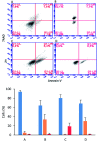
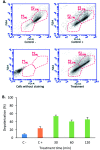
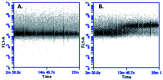
The cytotoxic effect of the tetrameric peptide LfcinB (20-25)4 against breast cancer cell line ATCC® HTB-22™ (MCF-7) was evaluated. The tetrameric peptide exhibited a concentration-dependent cytotoxic effect against MCF-7 cancer cells. The peptide at 22 µM had the maximum cytotoxic effect against MCF-7 cancer cells, reducing their cell viability to ∼20%. The cytotoxic effect of the tetrameric peptide against MCF-7 cells was sustained for 24 hours. Furthermore, the tetrameric peptide did not exhibit a significant cytotoxic effect against the non-tumorogenic trophoblastic cell line, which confirms their selectivity for breast cancer cell lines. The MCF-7 cells treated at 12.2 µM for 1 h exhibited morphological changes characteristic of apoptosis, such as rounded forms and cellular shrinkage. Furthermore, this peptide induces severe cellular damage to MCF-7 cells, mitochondrial membrane depolarization, and increase of cytoplasmic calcium concentration. Our results suggest that it has a significant selective cytotoxic effect against MCF-7 cells, which may be mainly associated with the apoptotic pathway. This peptide, which contains the RRWQWR motif, could be considered to be a promising candidate for developing therapeutic agents for the treatment of breast cancer.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Selective cytotoxic effect against the MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cell line of the antibacterial palindromic peptide derived from bovine lactoferricin.RSC Adv. 2020 May 6;10(30):17593-17601. doi: 10.1039/d0ra02688c. eCollection 2020 May 5. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35515633 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Synthetic Peptides Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibit Cytotoxic Effect against MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Molecules. 2017 Sep 29;22(10):1641. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101641. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28961215 Free PMC article.
-
A Tetrameric Peptide Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibits Specific Cytotoxic Effects against Oral Squamous-Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:630179. doi: 10.1155/2015/630179. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26609531 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides Derived from (RRWQWRMKKLG)2-K-Ahx Induce Selective Cellular Death in Breast Cancer Cell Lines through Apoptotic Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 26;21(12):4550. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124550. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32604743 Free PMC article.
-
A tetrameric peptide derived from bovine lactoferricin as a potential therapeutic tool for oral squamous cell carcinoma: A preclinical model.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 30;12(3):e0174707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174707. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28358840 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Soft Coral-Derived Dihydrosinularin Exhibits Antiproliferative Effects Associated with Apoptosis and DNA Damage in Oral Cancer Cells.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Sep 29;14(10):994. doi: 10.3390/ph14100994. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681218 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-penetrating peptides improve pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of anticancer drugs.Tissue Barriers. 2022 Jan 2;10(1):1965418. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2021.1965418. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Tissue Barriers. 2022. PMID: 34402743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-Resorcinarene Conjugates Obtained via Click Chemistry: Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;12(4):773. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040773. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107135 Free PMC article.
-
Nepenthes Extract Induces Selective Killing, Necrosis, and Apoptosis in Oral Cancer Cells.J Pers Med. 2021 Aug 31;11(9):871. doi: 10.3390/jpm11090871. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34575651 Free PMC article.
-
Selective cytotoxic effect against the MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cell line of the antibacterial palindromic peptide derived from bovine lactoferricin.RSC Adv. 2020 May 6;10(30):17593-17601. doi: 10.1039/d0ra02688c. eCollection 2020 May 5. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35515633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization, Breast Cancer, available on-line: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-cancers, accessed on 06 May 2019
-
- Winchester D., Hudis C. A. and Norton L., Breast Cancer, Ontario, BC Deeker Inc, 2006
-
- Richie R. C. Swanson J. O. J. Insur. Med. 2003;35:85–101. - PubMed
-
- Hormone Therapy for Breast Cancer, available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/treatment/hormone-therapy-fo..., accessed on 23 July 2017
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

