Effect of C-terminus amidation of Aβ39-42 fragment derived peptides as potential inhibitors of Aβ aggregation
- PMID: 35515767
- PMCID: PMC9055537
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04788k
Effect of C-terminus amidation of Aβ39-42 fragment derived peptides as potential inhibitors of Aβ aggregation
Abstract
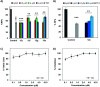
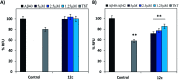
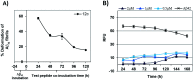
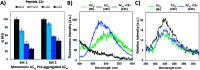
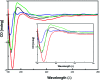
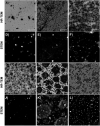
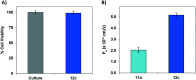
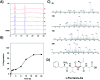
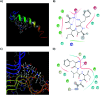
The C-terminus fragment (Val-Val-Ile-Ala) of amyloid-β is reported to inhibit the aggregation of the parent peptide. In an attempt to investigate the effect of sequential amino-acid scan and C-terminus amidation on the biological profile of the lead sequence, a series of tetrapeptides were synthesized using MW-SPPS. Peptide D-Phe-Val-Ile-Ala-NH2 (12c) exhibited high protection against β-amyloid-mediated-neurotoxicity by inhibiting Aβ aggregation in the MTT cell viability and ThT-fluorescence assay. Circular dichroism studies illustrate the inability of Aβ42 to form β-sheet in the presence of 12c, further confirmed by the absence of Aβ42 fibrils in electron microscopy experiments. The peptide exhibits enhanced BBB permeation, no cytotoxicity along with prolonged proteolytic stability. In silico studies show that the peptide interacts with the key amino acids in Aβ, which potentiate its fibrillation, thereby arresting aggregation propensity. This structural class of designed scaffolds provides impetus towards the rational development of peptide-based-therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease (AD).
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gaugler J. James B. Johnson T. Marin A. Weuve J. 2019 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's Dementia. 2019;15:321–387. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2019.01.010. - DOI
-
- Alzheimer's Association, Alzheimer's Disease Facts and Figures, 2019, Please see: http://www.alz.org/facts/, accessed on 20.05.2020
-
- Wong D. Rosenberg P. Zhou P. Kumar A. Raymont V. Ravert H. Dannals R. F. Nandi A. Brašić J. Ye W. Hilton J. In vivo imaging of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer disease using the radioligand 18F-AV-45 (flobetapir F-18) J. Nucl. Med. 2010;51:913–920. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.069088. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

