Understanding the relevance of protein corona in nanoparticle-based therapeutics and diagnostics
- PMID: 35515780
- PMCID: PMC9055466
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra05241h
Understanding the relevance of protein corona in nanoparticle-based therapeutics and diagnostics
Abstract
Over the past few decades, nanoparticle-based therapeutic and diagnostic systems have gained immense recognition. A relative improvement in the status of the global cancer burden has been successful due to the advent of nanoparticle-based formulations. However, exposure of nanoparticles (NPs) to a real-time biological media alters its native identity due to the formation of the biomolecular corona. Such biological interactions hinder the efficiency of the NPs system. The parameters that govern such intricate interaction are generally overlooked while designing nano drugs and delivery systems (nano-DDS). Fabricating nano-DDS with prolonged circulation time, enhanced drug-loading, and release capacity along with efficient clearance, remain the primary concerns associated with cancer therapeutics. This present review firstly aims to summarize the critical aspects that influence protein coronation on therapeutic nanoparticles designed for anti-cancer therapy. The role of protein corona in modifying the overall pharmacodynamics of the nanoparticle-based DDS has been discussed. Further, the studies and patents that extend the concept of protein corona into diagnostics have been elaborated. An understanding of the pros and cons associated with protein coronation would not only help us gain better insights into the fabrication of effective anti-cancer drug-delivery systems but also improve the shortcomings related to the clinical translation of these nanotherapeutics.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
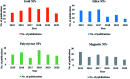


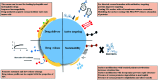



References
-
- Nguyen K. T. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011;2:103e.
-
- Khan I. Saeed K. Khan I. Arab. J. Chem. 2017;12:908–931. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

