Australian gridded chloride deposition-rate dataset
- PMID: 35515987
- PMCID: PMC9065633
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108189
Australian gridded chloride deposition-rate dataset
Abstract
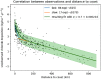
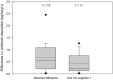
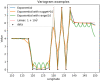
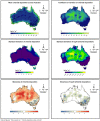
Chloride deposition-rate measurements at points within Australia are upscaled to the entire continent on a regular 0.05° grid. The upscaling uses a double-exponential correlation between deposition rate and distance to the coast, where the parameters in the double-exponential are spatially varying. These parameters are estimated using least-squares with Tikhonov regularisation to ensure minimal spatial variability. A calibration-constrained, null-space Monte-Carlo analysis is used to quantify uncertainty in the prediction. The resulting dataset consists of the best-fit chloride deposition rates across Australia, as well as estimates of uncertainty. The dataset can be used for various purposes including: estimating groundwater recharge through the use of the chloride mass-balance method; catchment salt balance estimates; regional investigations of groundwater hydrochemistry; and, corrosion prediction.
Keywords: Atmospheric chemistry; Chloride mass balance; Groundwater recharge; Hydrochemistry; Rainfall.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Davies P.J., Crosbie R.S. Mapping the spatial distribution of chloride deposition across Australia. J. Hydrol. 2018;561:76–88.
-
- Blackburn G., McLeod S. Salinity of atmospheric precipitation in the Murray-Darling drainage division, Australia. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1983;21:411–434.
-
- Biggs A.J.W. Rainfall salt accessions in the Queensland Murray-Darling basin. Soil Res. 2006;44:637–645.
-
- Sweeney M.E., Moore C.L., McQueen K.G., Spandler T. Geomorphic controls on deposition of salt in the greater tamar catchment, northeast Tasmania. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2016;64:1–12.
-
- M. Keywood, Origins and sources of atmospheric precipitation from australia: chlorine-36 and major-element chemistry, PhD thesis, Australian National University, 1995.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

