RNA-Seq data of ALKBH5 and FTO double knockout HEK293T human cells
- PMID: 35516002
- PMCID: PMC9062317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108187
RNA-Seq data of ALKBH5 and FTO double knockout HEK293T human cells
Abstract
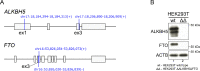
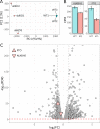
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant, highly dynamic mRNA modification that regulates mRNA splicing, stability, and translation. The m6A epigenetic mark is erased by RNA demethylases ALKBH5 (AlkB Homolog 5) and FTO (Fat mass and obesity-associated protein). The ALKBH5 and FTO RNA demethylases recognize m6A in similar nucleotide contexts. Therefore, these proteins can partially substitute for each other. To assess the impact of total m6A demethylation failure we performed high-throughput sequencing of cytoplasmic RNA from ALKBH5 and FTO double knockout and wild type HEK293T cells. The RNA-Seq libraries were sequenced on Illumina NextSeq 500, trimmed, and mapped to the human genome. The consequent read counting and differential expression analysis in the R environment detected 5871 differentially expressed and 166 alternatively spliced genes comparing double knockout against wild type HEK293T cells. Raw data are deposited in NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) repository under GEO accession GSE198050.
Keywords: ALKBH5; Demethylase; Epitranscriptomics; FTO; RNA modifications; Transcriptome; m6A demethylation; m6A methylation.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decreased ALKBH5, FTO, and YTHDF2 in Peripheral Blood Are as Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Aug 20;2020:5735279. doi: 10.1155/2020/5735279. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32884942 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Distinct RNA N-demethylation pathways catalyzed by nonheme iron ALKBH5 and FTO enzymes enable regulation of formaldehyde release rates.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 13;117(41):25284-25292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007349117. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32989163 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulated FTO and ALKBH5 co-operatively activates FOXO signaling through m6A methylation modification in HK2 mRNA mediated by IGF2BP2 to enhance glycolysis in colorectal cancer.Cell Biosci. 2023 Aug 14;13(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01100-9. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37580808 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances of m6A Demethylases Inhibitors and Their Biological Functions in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 22;23(10):5815. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105815. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of N6-Methyladenosine Demethylases and Its Interaction with Environmental Toxicants in Digestive System Cancers.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Sep 9;13:7101-7114. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S328188. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34526822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological interpretation of DNA/RNA modification by ALKBH proteins and their role in human cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jun 6;30(1):458. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02735-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40481562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine RNA methyltransferase CpMTA1 mediates CpAphA mRNA stability through a YTHDF1-dependent m6A modification in the chestnut blight fungus.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Aug 19;20(8):e1012476. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012476. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39159278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J., Li Y., Wang P., Han G., Zhang T., Chang J., Yin R., Shan Y., Wen J., Xie X., Feng M., Wang Q., Hu J., Cheng Y., Zhang T., Li Y., Gao Z., Guo C., Wang J., Liang J., Cui M., Gao K., Chai J., Liu W., Cheng H., Li L., Zhou F., Liu L., Luo Y., Li S., Zhang H. Leukemogenic chromatin alterations promote AML leukemia stem cells via a KDM4C-ALKBH5-AXL signaling axis. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27:81–97. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.04.001. .e8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Campos M.A., Edelheit S., Toth U., Safra M., Shachar R., Viukov S., Winkler R., Nir R., Lasman L., Brandis A., Hanna J.H., Rossmanith W., Schwartz S. Deciphering the “m6A Code” via antibody-independent quantitative profiling. Cell. 2019;178:731–747. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.013. .e16. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

