Controlling rotary motion of molecular motors based on oxindole
- PMID: 35516070
- PMCID: PMC9003629
- DOI: 10.1039/d2qo00129b
Controlling rotary motion of molecular motors based on oxindole
Abstract
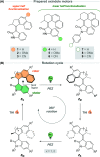
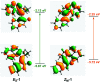
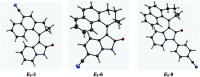
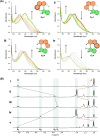
Molecular motors are essential components of artificial molecular machines, which can be used to manipulate and amplify mechanical motion at the nanoscale to create machine-like function. Since the discovery of light-driven rotary molecular motors, the field has been widely developed, including the introduction of molecular motors based on oxindole by our group in 2019. The rotational properties of molecular motors, e.g. absorption wavelength, quantum yield and rotation speed, often critically depend on substituent effects. Up to now, the substituent effects of oxindole-based molecular motors have not yet been investigated. Herein, we present a family of oxindole-based molecular motors functionalised at three different positions on the motor core, with either CN or OMe groups. The motors prepared in this work retain the favourable features of oxindole-based motors, i.e. simple synthesis and visible light addressability. We find that functionalisation has substantial effects on the absorption wavelength of the motors, meanwhile the rotation speed is unaffected. Furthermore, we found that functionalisation of the oxindole molecular motors increases their quantum efficiency considerably in comparison to previous motors of their class.
This journal is © the Partner Organisations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there to be no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of charge-transfer enhancement on the efficiency and rotary mechanism of an oxindole-based molecular motor.Chem Sci. 2021 Apr 29;12(21):7486-7497. doi: 10.1039/d1sc01105g. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34163839 Free PMC article.
-
Visible-Light-Driven Tunable Molecular Motors Based on Oxindole.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 May 8;141(18):7622-7627. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b03237. Epub 2019 Apr 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 31017421 Free PMC article.
-
Third-Generation Light-Driven Symmetric Molecular Motors.J Am Chem Soc. 2017 Jul 19;139(28):9650-9661. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b04412. Epub 2017 Jul 5. J Am Chem Soc. 2017. PMID: 28628318 Free PMC article.
-
Designing light-driven rotary molecular motors.Chem Sci. 2021 Oct 20;12(45):14964-14986. doi: 10.1039/d1sc04781g. eCollection 2021 Nov 24. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34909140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the mechanism of ATP-driven rotary motors from direct torque measurement.Biophys Rev. 2019 Aug;11(4):653-657. doi: 10.1007/s12551-019-00564-9. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Biophys Rev. 2019. PMID: 31321734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coupled Rocking Motion in a Light-Driven Rotary Molecular Motor.J Org Chem. 2024 Jan 5;89(1):1-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c01830. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Org Chem. 2024. PMID: 36223433 Free PMC article.
-
A visible-light-driven molecular motor based on barbituric acid.Chem Sci. 2023 Jul 20;14(32):8458-8465. doi: 10.1039/d3sc03090c. eCollection 2023 Aug 16. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37592992 Free PMC article.
-
Photoswitchable Molecular Motor Phospholipid: Synthesis, Characterization, and Integration into Lipid Vesicles.Langmuir. 2025 Feb 18;41(6):3961-3970. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c04173. Epub 2025 Feb 3. Langmuir. 2025. PMID: 39900533 Free PMC article.
-
Coupled Rotary Motion in Molecular Motors.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Feb 28;146(8):5634-5642. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c14430. Epub 2024 Feb 13. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38350104 Free PMC article.
-
Solvent-Dependent Ultrafast Photochemical Dynamics of N-Methyl Oxindole Overcrowded Alkene Molecular Motors.J Phys Chem A. 2025 Jun 26;129(25):5530-5544. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.5c02679. Epub 2025 Jun 15. J Phys Chem A. 2025. PMID: 40518630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Browne W. R. and Feringa B. L., Molecular Switches, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2011
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
