Dye degradation performance, bactericidal behavior and molecular docking analysis of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles
- PMID: 35516171
- PMCID: PMC9055104
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04851h
Dye degradation performance, bactericidal behavior and molecular docking analysis of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles
Abstract
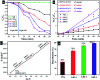
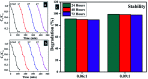
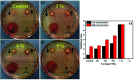
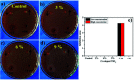
Copper-doped TiO2 was prepared with a sol-gel chemical method. Various concentrations (3, 6, and 9 wt%) of Cu dopant were employed. Several techniques were implemented to assess the structural, optical, morphological and chemical properties of the synthesized samples. Evaluation of elemental composition using SEM-EDS and XRF techniques showed the presence of dopant element in the prepared samples. XRD analysis confirmed the presence of anatase (TiO2) phase with interstitial doping. Incorporation of dopant was observed to enhance the crystallinity and increase the crystallite size of the synthesized products. SAED profiles revealed a high degree of crystallinity in the prepared specimens, which was also evident in the XRD spectra. Optical properties studied using UV-vis spectroscopy depicted a shift of the maximum absorption to the visible region (redshift) that signified a reduction in the band gap energy of Cu-doped TiO2 samples. Examination of morphological features with scanning and high-resolution transmission electron microscopes revealed the formation of spherical nanoparticles with a tendency to agglomerate with increasing dopant concentration. Molecular vibrations and the formation of Ti-O-Ti bonds were revealed through FTIR spectra. PL spectroscopy recorded the trapping efficiency and migration of charge carriers, which exhibited electron-hole recombination behavior. Doped nanostructures showed enhanced bactericidal performance and synergism against S. aureus and E. coli. In summary, Cu-doped TiO2 nanostructures were observed to impede bacteria effectively, which is deemed beneficial in overcoming ailments caused by pathogens such as microbial etiologies. Furthermore, molecular docking analysis was conducted to study the interaction of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles with multiple proteins namely β-lactamase (binding score: -4.91 kcal mol-1), ddlB (binding score: -5.67 kcal mol-1) and FabI (binding score: -6.13 kcal mol-1) as possible targets with active site residues. Dye degradation/reduction of control and Cu-doped samples were studied through absorption spectroscopy. The obtained outcomes of the performed experiment indicated that the photocatalytic activity of Cu-TiO2 enhanced with increasing dopant concentration, which is thought to be due to a decreased rate of electron-hole pair recombination. Consequently, it is suggested that Cu-TiO2 can be exploited as an effective candidate for antibacterial and dye degradation applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Photocatalytic and bactericidal properties and molecular docking analysis of TiO2 nanoparticles conjugated with Zr for environmental remediation.RSC Adv. 2020 Aug 14;10(50):30007-30024. doi: 10.1039/d0ra05862a. eCollection 2020 Aug 10. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35518250 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen and Carbon Nitride-Doped TiO2 for Multiple Catalysis and Its Antimicrobial Activity.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021 Jul 26;16(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s11671-021-03573-4. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021. PMID: 34312737 Free PMC article.
-
Photocatalytic, dye degradation, and bactericidal behavior of Cu-doped ZnO nanorods and their molecular docking analysis.Dalton Trans. 2020 Jun 23;49(24):8314-8330. doi: 10.1039/d0dt01397h. Dalton Trans. 2020. PMID: 32515772
-
Molybdenum-doped iron oxide nanostructures synthesized via a chemical co-precipitation route for efficient dye degradation and antimicrobial performance: in silico molecular docking studies.RSC Adv. 2022 Dec 9;12(54):35177-35191. doi: 10.1039/d2ra07238f. eCollection 2022 Dec 6. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36540207 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring structural and optical properties of iodine-doped TiO2 nanoparticles in Rhodamine-B dye degradation: Experimental and theoretical investigation.Chemosphere. 2024 Sep;364:143183. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.143183. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Chemosphere. 2024. PMID: 39214412
Cited by
-
Photocatalytic and bactericidal properties and molecular docking analysis of TiO2 nanoparticles conjugated with Zr for environmental remediation.RSC Adv. 2020 Aug 14;10(50):30007-30024. doi: 10.1039/d0ra05862a. eCollection 2020 Aug 10. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35518250 Free PMC article.
-
A State-of-Art Review of the Metal Oxide-Based Nanomaterials Effect on Photocatalytic Degradation of Malachite Green Dyes and a Bibliometric Analysis.Glob Chall. 2023 Apr 27;7(6):2300001. doi: 10.1002/gch2.202300001. eCollection 2023 Jun. Glob Chall. 2023. PMID: 37287595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly efficient visible light active Cu-ZnO/S-g-C3N4 nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants.RSC Adv. 2021 Nov 19;11(59):37254-37267. doi: 10.1039/d1ra07203j. eCollection 2021 Nov 17. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35496420 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Bi Doping into Boron Nitride Nanosheets on Electronic and Optical Properties Using Theoretical Calculations and Experiments.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021 May 12;16(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s11671-021-03542-x. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021. PMID: 33978872 Free PMC article.
-
Photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of graphene oxide/cellulose-doped TiO2 quantum dots: in silico molecular docking studies.Nanoscale Adv. 2022 Jul 27;4(18):3764-3776. doi: 10.1039/d2na00383j. eCollection 2022 Sep 13. Nanoscale Adv. 2022. PMID: 36133332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raza A. Ikram M. Aqeel M. Imran M. Ul-Hamid A. Riaz K. N. Ali S. Enhanced industrial dye degradation using Co doped in chemically exfoliated MoS2 nanosheets. Appl. Nanosci. 2020;10:1535–1544. doi: 10.1007/s13204-019-01239-3. - DOI
-
- Moma J. and Baloyi J., Modified Titanium Dioxide for Photocatalytic Applications, in Photocatalysts - Applications and Attributes, ed. S. Bahadar Khan and K. Akhtar, IntechOpen, 2019
-
- Sharma M. Behl K. Nigam S. Joshi M. TiO2-GO nanocomposite for energy and environmental applications: a green synthesis approach. Vacuum. 2018;156:434–439. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.08.009. - DOI
-
- Kavitha V. Ramesh P. S. Geetha D. Synthesis of Cu Loaded TiO2 Nanoparticles for the Improved Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B. Int. J. Nanosci. 2016;15:1660002. doi: 10.1142/S0219581X16600024. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

