New chalcone derivatives: synthesis, antiviral activity and mechanism of action
- PMID: 35516226
- PMCID: PMC9055036
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra03684f
New chalcone derivatives: synthesis, antiviral activity and mechanism of action
Abstract
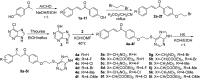
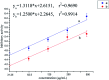
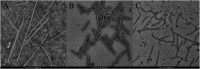
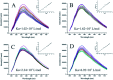
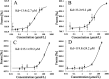
In this work, twenty-eight chalcone derivatives containing a purine (sulfur) ether moiety were synthesized and their antiviral activities were evaluated. Biological results showed that compound 5d exhibited outstanding inactive activity against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) in vivo (EC50 = 65.8 μg mL-1), which is significantly superior to that of ribavirin (EC50 = 154.3 μg mL-1). Transmission electron microscopy indicated that compound 5d can break the integrity of TMV particles. The results of microscale thermophoresis, fluorescence titration and molecular docking showed that compound 5d had stronger combining affinity (K a = 1.02 ×105 L mol-1, K d = 13.4 μmol L-1) with TMV coat protein (TMV-CP), which is due to the formation of five hydrogen bonds between compound 5d and the amino-acid residues of TMV-CP. These findings revealed that compound 5d can effectively inhibit the infective ability of TMV. This work provides inspiration and reference for the discovery of new antiviral agents.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

