Highly effective photocatalytic performance of {001}-TiO2/MoS2/RGO hybrid heterostructures for the reduction of Rh B
- PMID: 35516304
- PMCID: PMC9064259
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra02634g
Highly effective photocatalytic performance of {001}-TiO2/MoS2/RGO hybrid heterostructures for the reduction of Rh B
Abstract
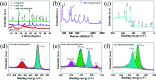
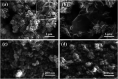
Effective separation and rapid transfer of photogenerated electron-hole pairs are key features of photocatalytic materials with high catalytic activity, which could be achieved in co-catalysts. It is reported that the two-dimensional (2D) MoS2 is a promising co-catalyst due to its unique semi-conductive properties and graphene-like layered structure. However, the application of MoS2 as a co-catalyst is limited by its poor electrical conductivity. On the other hand, it is worth noting that TiO2 possesses reactive crystal facets, which is one of the dominant mechanisms for the separation of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. In this work, we prepared MoS2/RGO hybrids as co-catalysts which were doped to TiO2 with highly reactive {001} planes via the hydrothermal method. It was found that the {001}-TiO2/MoS2/RGO photocatalysts with 7 wt% MoS2/RGO co-catalyst show the highest photodegradation activity for the degradation of Rh B under visible light irradiation (λ > 400 nm), which could result from the synergy of the effective separation of electron-hole pairs by the {001} facets in TiO2 and the rapid transfer of electron-hole pairs in MoS2/RGO. The results show that the {001}-TiO2/MoS2/RGO hybrid is a low-cost and stable photocatalyst for the effective degradation of Rh B under visible light.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict in the statement.
Figures




Similar articles
-
From Pollutant Removal to Renewable Energy: MoS2-Enhanced P25-Graphene Photocatalysts for Malathion Degradation and H2 Evolution.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jun 3;18(11):2602. doi: 10.3390/ma18112602. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508601 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of flower-like MoS2/Fe3O4/rGO composite with enhanced photo-Fenton like catalyst performance.RSC Adv. 2018 Oct 30;8(64):36625-36631. doi: 10.1039/c8ra06537c. eCollection 2018 Oct 26. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35558923 Free PMC article.
-
Cu2ZnSnS4/MoS2-Reduced Graphene Oxide Heterostructure: Nanoscale Interfacial Contact and Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 3;7:39411. doi: 10.1038/srep39411. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28045066 Free PMC article.
-
MoS2 as a Co-Catalyst for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production: A Mini Review.Molecules. 2022 May 20;27(10):3289. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103289. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35630769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) based photoredox catalysis in chemical transformations.RSC Adv. 2022 Oct 18;12(46):29826-29839. doi: 10.1039/d2ra05695j. eCollection 2022 Oct 17. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36321108 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zn/Cr-MOFs/TiO2 Composites as Adsorbents for Levofloxacin Hydrochloride Removal.Molecules. 2024 Sep 20;29(18):4477. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184477. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339472 Free PMC article.
-
From Pollutant Removal to Renewable Energy: MoS2-Enhanced P25-Graphene Photocatalysts for Malathion Degradation and H2 Evolution.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jun 3;18(11):2602. doi: 10.3390/ma18112602. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoffmann M. R. Choi W. Bahnemann D. W. Chem. Rev. 1995;95:69–96. doi: 10.1021/cr00033a004. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

