Effect and Significance of High-Quality Nursing on Blood Glucose, Pregnancy Outcome, and Neonatal Complications of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 35516455
- PMCID: PMC9064497
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2426417
Effect and Significance of High-Quality Nursing on Blood Glucose, Pregnancy Outcome, and Neonatal Complications of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effect and Significance of High-Quality Nursing on Blood Glucose, Pregnancy Outcome, and Neonatal Complications of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9782396. doi: 10.1155/2023/9782396. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 38094372 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To explore the role of high-quality nursing on blood glucose, pregnancy outcome, and neonatal complications in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus.
Methods: Altogether, 148 patients with GDM admitted to our hospital were selected as the research participants, 83 of whom received high-quality nursing as the observation group (OG). Another 65 patients received only routine care as the control group (CG). The blood sugar level, blood pressure value, and adverse pregnancy outcomes of the OG and the CG of patients after intervention were compared. The changes of psychological state and nursing satisfaction of the OG and the CG of patients were observed. The blood lipid level and neonatal complications of the OG and the CG were detected.
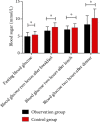
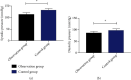
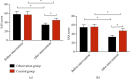
Results: The blood sugar level of the OG was lower than that of the CG (P < 0.05). The systolic pressure and diastolic pressure of patients in the OG were lower than those in the CG after nursing intervention (P < 0.05). The abnormal delivery rate in the CG was evidently higher than that in the OG (P < 0.05). After intervention, SAS and SDS scores in the OG were lower than those in the CG (P < 0.05). The number of people who needed improvement and were dissatisfied in the OG was evidently lower than that in the CG (P < 0.05). TG and LDL-C in the OG were lower than those in the CG (P < 0.05). The total incidence of complications in the CG was evidently higher than that in the OG (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: High-quality nursing can reduce blood sugar and blood pressure of GDM patients and has a great protective effect on maternal and infant health, which is worthy of clinical practice.
Copyright © 2022 Wenjuan Zhong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of preventive nursing based on quantitative evaluation on psychological state and maternal-infant outcome in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023 Dec;36(1):2183473. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2023.2183473. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023. PMID: 36987871
-
Prone position nursing combined with ECMO intervention prevent patients with severe pneumonia from complications and improve cardiopulmonary function.Am J Transl Res. 2021 May 15;13(5):4969-4977. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34150081 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Multidisciplinary Team Continuous Nursing on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism, Pregnancy Outcome, and Neonatal Immune Function in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Dis Markers. 2022 Sep 8;2022:7285639. doi: 10.1155/2022/7285639. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36118671 Free PMC article.
-
[Gestational diabetes mellitus (Update 2019)].Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2019 May;131(Suppl 1):91-102. doi: 10.1007/s00508-018-1419-8. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2019. PMID: 30980150 Review. German.
-
Fetal biometry for guiding the medical management of women with gestational diabetes mellitus for improving maternal and perinatal health.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 3;9(9):CD012544. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012544.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31476798 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Effect and Significance of High-Quality Nursing on Blood Glucose, Pregnancy Outcome, and Neonatal Complications of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9782396. doi: 10.1155/2023/9782396. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 38094372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilbert L., Gross J., Lanzi S., Quansah D. Y., Puder J., Horsch A. How diet, physical activity and psychosocial well-being interact in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: an integrative review. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth . 2019;19(1):p. 60. doi: 10.1186/s12884-019-2185-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Han S., Middleton P., Shepherd E., van Ryswyk E., Crowther C. A., Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group Different types of dietary advice for women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews . 2017;2017(4):p. 2. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009275.pub3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

