Natural product diversity from the endophytic fungi of the genus Aspergillus
- PMID: 35516645
- PMCID: PMC9054607
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04290k
Natural product diversity from the endophytic fungi of the genus Aspergillus
Abstract
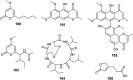
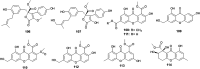
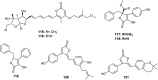
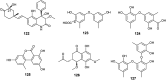
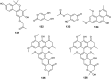
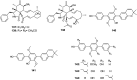
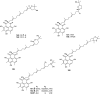
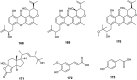
The endophytic fungus Aspergillus is considered as an enormous source of chemical leads with promising biological activities. Different Aspergillus species have proved their ability to produce plenty of secondary metabolites including butenolides, alkaloids, terpenoids, cytochalasins, phenalenones, ρ-terphenyls, xanthones, sterols, diphenyl ether and anthraquinone derivatives with diverse biological activities, such as anti-cancer, antifungal, anti-bacterial, anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, antitrypanosomal and antileishmanial activities. From January 2015 until December 2019, three hundred and sixty-one secondary metabolites were reported from different endophytic Aspergillus species. This review discusses the isolated secondary metabolites from different endophytic Aspergillus species reported from January 2015 to December 2019 along with their reported biological activities and structural aspects whenever applicable.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
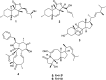
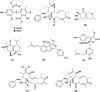

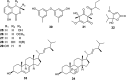

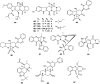
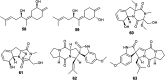

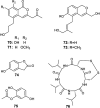

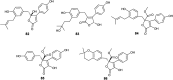
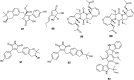




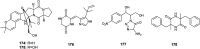



References
-
- Soltani J., New Futur. Dev. Microb. Biotechnol. Bioeng., Elseiver, 2016, pp. 275–292
-
- Sadorn K. Saepua S. Boonyuen N. Laksanacharoen P. Rachtawee P. Prabpai S. Kongsaeree P. Pittayakhajonwut P. Tetrahedron. 2016;72:489–495. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2015.11.056. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

