Overall Survival Benefits of First-Line Treatments for Asian Patients With Advanced EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Harboring L858R Mutation: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35516725
- PMCID: PMC9065903
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2022.100322
Overall Survival Benefits of First-Line Treatments for Asian Patients With Advanced EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Harboring L858R Mutation: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Randomized controlled trials have investigated different first-line treatments for patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Nevertheless, their efficacy, in particular, the long-term overall survival (OS) benefit in Asian patients with L858R mutation, remains unclear.
Methods: We performed a systematic review and frequentist network meta-analysis by retrieving relevant literature from PubMed/MEDLINE, Ovid, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, trial registries, and other sources. We included randomized controlled trials comparing two or more treatments in the first-line setting for Asian patients with L858R mutation. This study was registered in the Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD 42022295897).
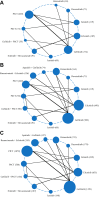
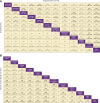
Results: There were a total of 18 trials that involved 1852 Asian patients and 12 treatments, including the following: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) (osimertinib, dacomitinib, afatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, and icotinib), pemetrexed-based chemotherapy, pemetrexed-free chemotherapy, and combination treatments (gefitinib plus apatinib, erlotinib plus ramucirumab, erlotinib plus bevacizumab and gefitinib plus pemetrexed-based chemotherapy). Asian patients with L858R mutation had no significant OS benefits from all these treatments. Gefitinib plus pemetrexed-based chemotherapy, dacomitinib, osimertinib, and erlotinib plus bevacizumab were found to be consistent in yielding the best progression-free survival benefit (p scores = 93%, 79%, 77%, and 70%). Combination treatments caused more toxicity, especially erlotinib plus bevacizumab and gefitinib plus pemetrexed-based chemotherapy, resulting in the greatest incidence of grade greater than or equal to 3 adverse events.
Conclusions: In Asian patients harboring L858R mutation, EGFR TKIs and combination treatments had no OS benefit when compared with conventional chemotherapies. Further studies are warranted to investigate the resistance mechanism with TKIs and potential combination strategies in patients with this common but less favorable mutation.
Keywords: Asian; Epidermal growth factor receptor; L858R mutation; Non–small-cell lung cancer; Tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overall Survival Benefits of First-Line Treatments for Asian Patients with Advanced Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated NSCLC Harboring Exon 19 Deletion: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 11;14(14):3362. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143362. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of first line treatments for patients with advanced epidermal growth factor receptor mutated, non-small cell lung cancer: systematic review and network meta-analysis.BMJ. 2019 Oct 7;367:l5460. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l5460. BMJ. 2019. PMID: 31591158 Free PMC article.
-
First-line therapeutic strategy for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with Leu858Arg epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: a Bayesian network meta-analysis.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022 Oct 17;13:20406223221125706. doi: 10.1177/20406223221125706. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022. PMID: 36274751 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the efficacy and safety of first-line treatments for of advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in Asian populations: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1212313. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1212313. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37484016 Free PMC article.
-
Pemetrexed/carboplatin plus gefitinib as a first-line treatment for EGFR-mutant advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer: a Bayesian network meta-analysis.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2019 Dec 30;11:1758835919891652. doi: 10.1177/1758835919891652. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31908655 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Overall Survival Benefits of First-Line Treatments for Asian Patients with Advanced Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated NSCLC Harboring Exon 19 Deletion: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 11;14(14):3362. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143362. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-to-Event Modeling for Survival Prediction of Osimertinib as the First- and Second-Line Therapy.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 9;14(12):4077. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124077. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40565824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated lung carcinomas with insufficient response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors.Future Oncol. 2024;20(31):2397-2407. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2386925. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Future Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39229777 Review.
-
Comparing Gefitinib and Traditional Chemotherapy for Better Survival in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Jan 12;15(1):e33691. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33691. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36788891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osimertinib is associated with improved outcomes in pre-treated non-small cell lung cancer leptomeningeal metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysiss.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 17;10(9):e29668. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29668. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38698967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization International Agency for Research on Cancer. Globocan worldwide fact sheet 2018. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/900-world-fact-she... Accessed December 2021.
-
- World Health Organization International Agency for Research on Cancer. Globocan Asia fact sheet 2018. http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/935-asia-fact-sheet... Accessed December 2021.
-
- Herbst R.S., Morgensztern D., Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553:446–454. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

