Pirfenidone for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Beyond
- PMID: 35516794
- PMCID: PMC9062707
- DOI: 10.15420/cfr.2021.30
Pirfenidone for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Beyond
Abstract
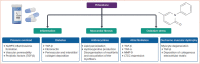
Pirfenidone (PFD) slows the progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) by inhibiting the exaggerated fibrotic response and possibly through additional mechanisms, such as anti-inflammatory effects. PFD has also been evaluated in other fibrosing lung diseases. Myocardial fibrosis is a common feature of several heart diseases and the progressive deposition of extracellular matrix due to a persistent injury to cardiomyocytes may trigger a vicious cycle that leads to persistent structural and functional alterations of the myocardium. No primarily antifibrotic medications are used to treat patients with heart failure. There is some evidence that PFD has antifibrotic actions in various animal models of cardiac disease and a phase II trial on patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction has yielded positive results. This review summarises the evidence about the possible mechanisms of IPF and modulation by PFD, the main results about IPF or non-IPF interstitial pneumonias and also data about PFD as a potential protective cardiac drug.
Keywords: Pirfenidone; animal models; clinical trials; heart; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; lung.
Copyright © 2022, Radcliffe Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Iyer SN, Wild JS, Schiedt MJ et al. Dietary intake of pirfenidone ameliorates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in hamsters. J Lab Clin Med. 1995;125:779–85. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188:733–48. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources