Droplet microfluidics: fundamentals and its advanced applications
- PMID: 35516933
- PMCID: PMC9055587
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04566g
Droplet microfluidics: fundamentals and its advanced applications
Erratum in
-
Correction: Droplet microfluidics: fundamentals and its advanced applications.RSC Adv. 2020 Sep 3;10(54):32843-32844. doi: 10.1039/d0ra90086a. eCollection 2020 Sep 1. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35557504 Free PMC article.
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Droplet microfluidics: fundamentals and its advanced applications.RSC Adv. 2022 Dec 1;12(53):34566. doi: 10.1039/d2ra90125k. eCollection 2022 Nov 29. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36545627 Free PMC article.
Abstract
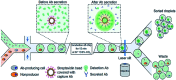
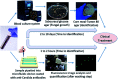
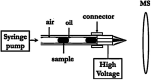
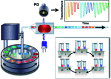
Droplet-based microfluidic systems have been shown to be compatible with many chemical and biological reagents and capable of performing a variety of operations that can be rendered programmable and reconfigurable. This platform has dimensional scaling benefits that have enabled controlled and rapid mixing of fluids in the droplet reactors, resulting in decreased reaction times. This, coupled with the precise generation and repeatability of droplet operations, has made the droplet-based microfluidic system a potent high throughput platform for biomedical research and applications. In addition to being used as micro-reactors ranging from the nano- to femtoliter (10-15 liters) range; droplet-based systems have also been used to directly synthesize particles and encapsulate many biological entities for biomedicine and biotechnology applications. For this, in the following article we will focus on the various droplet operations, as well as the numerous applications of the system and its future in many advanced scientific fields. Due to advantages of droplet-based systems, this technology has the potential to offer solutions to today's biomedical engineering challenges for advanced diagnostics and therapeutics.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
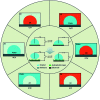
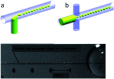
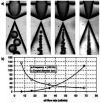

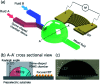
References
-
- Manz A. Graber N. Widmer H. M. Sens. Actuators, B. 1990;1:244–248. doi: 10.1016/0925-4005(90)80209-I. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

