Nanocarriers for ocular drug delivery: current status and translational opportunity
- PMID: 35516960
- PMCID: PMC9055630
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04971a
Nanocarriers for ocular drug delivery: current status and translational opportunity
Abstract
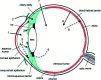
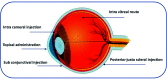
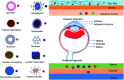
Ocular diseases have a significant effect on vision and quality of life. Drug delivery to ocular tissues is a challenge to formulation scientists. The major barriers to delivering drugs to the anterior and posterior segments include physiological barriers (nasolacrimal drainage, blinking), anatomical barriers (static and dynamic), efflux pumps and metabolic barriers. The static barriers comprise the different layers of the cornea, sclera, and blood-aqueous barriers whereas dynamic barriers involve conjunctival blood flow, lymphatic clearance and tear drainage. The tight junctions of the blood-retinal barrier (BRB) restrict systemically administered drugs from entering the retina. Nanocarriers have been found to be effective at overcoming the issues associated with conventional ophthalmic dosage forms. Various nanocarriers, including nanodispersion systems, nanomicelles, lipidic nanocarriers, polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, niosomes, and dendrimers, have been investigated for improved permeation and effective targeted drug delivery to various ophthalmic sites. In this review, various nanomedicines and their application for ophthalmic delivery of therapeutics are discussed. Additionally, scale-up and clinical status are also addressed to understand the current scenario for ophthalmic drug delivery.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO, International Classification of Diseases, 11th Revision (ICD-11), https://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/, 2019
-
- Patel U., Boucher M., de Léséleuc L. and Visintini S., Voretigene Neparvovec: An Emerging Gene Therapy for the Treatment of Inherited Blindness, Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health, 2016 - PubMed
-
- ReSure® Sealant – Ocular Therapeutix, https://www.ocutx.com/products/resure-sealant/, accessed 30 June 2020
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

