Sustainable waste management and recycling of Zn-Al layered double hydroxide after adsorption of levofloxacin as a safe anti-inflammatory nanomaterial
- PMID: 35516965
- PMCID: PMC9055605
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04898d
Sustainable waste management and recycling of Zn-Al layered double hydroxide after adsorption of levofloxacin as a safe anti-inflammatory nanomaterial
Erratum in
-
Correction: Sustainable waste management and recycling of Zn-Al layered double hydroxide after adsorption of levofloxacin as a safe anti-inflammatory nanomaterial.RSC Adv. 2020 Aug 6;10(49):29128. doi: 10.1039/d0ra90083d. eCollection 2020 Aug 5. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35532482 Free PMC article.
Abstract
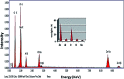
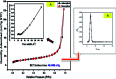
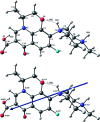
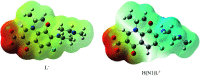
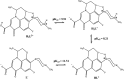
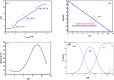
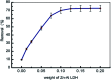
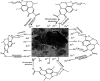
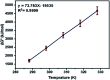
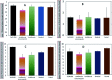
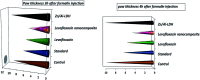
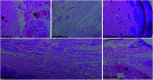
Inorganic nano-layered double hydroxide (LDH) materials are used in the catalytic field, and have demonstrated great applicability in the pharmacological fields. In the current study, we report Zn-Al LDH as an adsorbent for levofloxacin (levo). The physical and chemical properties of the prepared material before and after adsorption were monitored using X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopic analysis, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area measurements, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). Density functional theory (DFT) calculations for levo and its protonated species were studied at the B3LYP/6-311G (d,p) level of theory. The removal percentage of levo was 73.5%. The adsorption isotherm was investigated using nine different models at pH 9, where the obtained correlation coefficients (R 2) using the Redlich-Peterson and Toth models were 0.977. The thermodynamic parameters ΔS°, ΔG° and ΔH° were estimated and discussed in detail. Also, to support the adsorption research field, the applicability of the formed waste after the adsorption of levo onto Zn-Al LDH was investigated for medical purposes. The toxicity of levo in both normal and nanocomposite form was studied. Neither toxicological symptoms nor harmless effects were exhibited throughout the in vivo study. The oral anti-inflammatory activity, tested using 6% formalin to produce edema in the footpad, was manifested as a significant increase of 37% in the anti-inflammatory effect of the Zn-Al LDH/levo nanocomposite compared to levo in its normal form.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

