Investigation of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory tri-peptides: a combination of 3D-QSAR and molecular docking simulations
- PMID: 35517085
- PMCID: PMC9056908
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra05119e
Investigation of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory tri-peptides: a combination of 3D-QSAR and molecular docking simulations
Abstract
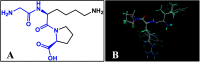
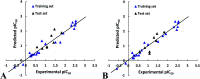
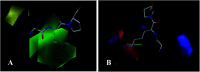
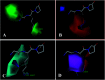
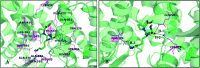
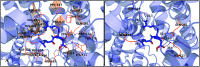
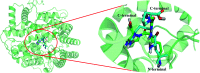
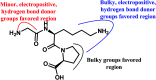
Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) is a key enzyme in the regulation of peripheral blood pressure and electrolyte homeostasis. Therefore, ACE is considered as a promising target for treatment of hypertension. In the present work, in order to investigate the binding interactions between ACE and tri-peptides, three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) models using comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) methods were developed. Three different alignment methods (template ligand-based, docking-based, and common scaffold-based) were employed to construct reliable 3D-QSAR models. Statistical parameters derived from the QSAR models indicated that the template ligand-based CoMFA (R cv 2 = 0.761, R pred 2 = 0.6257) and CoMSIA (R cv 2 = 0.757, R pred 2 = 0.6969) models were better than the other alignment-based models. In addition, molecular docking studies were carried out to predict the binding modes of the peptides to ACE. The peptide-enzyme interactions were consistent with the derived 3D contour maps. Overall, the insights gained from this study would offer theoretical references for understanding the mechanism of action of tri-peptides when binding to ACE and aid in the design of more potent tri-peptides.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of the Structural Features of Guanine Derivatives as MGMT Inhibitors Using 3D-QSAR Modeling Combined with Molecular Docking.Molecules. 2016 Jun 23;21(7):823. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070823. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27347909 Free PMC article.
-
In silico design of novel FAK inhibitors using integrated molecular docking, 3D-QSAR and molecular dynamics simulation studies.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Aug;40(13):5965-5982. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1875880. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33475043
-
Insight into structural requirements of ACE inhibitory dipeptides: QSAR and molecular docking studies.Mol Divers. 2020 Nov;24(4):957-969. doi: 10.1007/s11030-019-10005-0. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Mol Divers. 2020. PMID: 31655961
-
CoMFA and CoMSIA 3D QSAR and docking studies on conformationally-restrained cinnamoyl HIV-1 integrase inhibitors: exploration of a binding mode at the active site.J Med Chem. 2002 Feb 14;45(4):841-52. doi: 10.1021/jm010399h. J Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 11831895
-
Considerations for Docking of Selective Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors.Molecules. 2020 Jan 11;25(2):295. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020295. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31940798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- López-Fandio R. Otte J. Camp J. V. Int. Dairy J. 2006;16:1293.
-
- Fitzgerald R. J. Murray B. A. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2006;59:118–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0307.2006.00250.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

