Iron oxide nanoparticle-induced hematopoietic and immunological response in rats
- PMID: 35517102
- PMCID: PMC9056920
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra05901c
Iron oxide nanoparticle-induced hematopoietic and immunological response in rats
Abstract
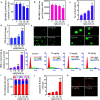
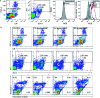
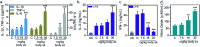
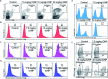
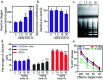
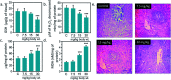
The application and use of iron oxide nanoparticless (IONPs) in the biomedical field are steadily increasing, although it remains uncertain whether IONPs are safe or should be used with caution. In the present study, we investigated the toxicity profile of ultrafine IONPs in rats administered with 7.5, 15 and 30 mg IONPs/kg body wt intravenously once a week for 4 weeks. IONP treatment reduces bone marrow-mononuclear cell proliferation, increases free radical species and DNA damage leading to growth arrest and subsequently apoptosis induction at 15 and 30 mg doses. It also induces apoptosis in undifferentiated hematopoietic stem cells. IONP treatment significantly increased the pro-inflammatory cytokine (Interleukin (IL)-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6) level in serum. The induction in inflammation was likely mediated by splenic M1 macrophages (IL-6 and TNF-α secretion). IONP treatment induces splenocyte apoptosis and alteration in the immune system represented by reduced CD4+/CD8+ ratio and increased B cells. It also reduces innate defense represented by lower natural killer cell cytotoxicity. IONP administration markedly increased lipid peroxidation in the spleen, while the glutathione level was reduced. Similarly, superoxide dismutase activity was increased and catalase activity was reduced in the spleen of IONP-treated rats. At an organ level, IONP treatment did not cause any significant injury or structural alteration in the spleen. Collectively, our results suggest that a high dose of ultrafine IONPs may cause oxidative stress, cell death, and inflammation in a biological system.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

