First-principles study of magnetism in some novel MXene materials
- PMID: 35517132
- PMCID: PMC9058502
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra03643a
First-principles study of magnetism in some novel MXene materials
Abstract
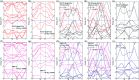
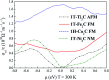
Magnetic two-dimensional materials have gained considerable attention in recent years due to their special topologies and promising applications in electronic and spintronic devices. As a new family of two-dimensional materials, MXene materials may have unusual magnetic properties. In this work, the structural stabilities and electronic properties of 1H and 1T type pristine M2C (M = Sc, Ti, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) MXenes with different magnetic configurations were calculated and compared. The critical temperatures of the magnetic MXenes were evaluated through Monte Carlo simulations using the spin-exchange coupling parameters. The results suggest that the ground-state 1T-Ti2C and 1T-Fe2C, 1H-Co2C MXenes are antiferromagnetic or ferromagnetic materials with high Néel or Curie temperatures. Different from the other pristine M2C MXenes with metallic properties, indirect band gaps were found for the 1T-Ti2C and 1T-Ni2C MXenes, which may be useful for their application in information storage or sensors. The findings are expected to promote the development of novel devices based on MXenes and their magnetic properties.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High Curie temperature and carrier mobility of novel Fe, Co and Ni carbide MXenes.Nanoscale. 2020 Jun 7;12(21):11627-11637. doi: 10.1039/c9nr10927g. Epub 2020 May 21. Nanoscale. 2020. PMID: 32436494
-
Computational design of double transition metal MXenes with intrinsic magnetic properties.Nanoscale Horiz. 2022 Feb 28;7(3):276-287. doi: 10.1039/d1nh00621e. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022. PMID: 35108718
-
Controlled 2H/1T phase transition in MoS2 monolayers by a strong interface with M2C MXenes: a computational study.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021 Sep 22;23(36):20107-20116. doi: 10.1039/d1cp02648h. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021. PMID: 34505593
-
Potential of MXenes as a novel material for spintronic devices: a review.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2023 Jul 19;25(28):18584-18608. doi: 10.1039/d3cp01261a. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2023. PMID: 37409617 Review.
-
Two-dimensional Ti3C2 MXene-based nanostructures for emerging optoelectronic applications.Mater Horiz. 2021 Nov 1;8(11):2929-2963. doi: 10.1039/d1mh00986a. Mater Horiz. 2021. PMID: 34558566 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and emerging challenges in MXenes and their nanocomposites for biosensing applications.RSC Adv. 2022 Jul 6;12(30):19590-19610. doi: 10.1039/d2ra02985e. eCollection 2022 Jun 29. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35865615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theoretical Analysis of Magnetic Coupling in the Ti2C Bare MXene.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2023 Feb 14;127(7):3706-3714. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c07609. eCollection 2023 Feb 23. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 36865991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tan C. Cao X. Wu X. He Q. Yang J. Zhang X. Chen J. Zhao W. Han S. Nam G. Sindoro M. Zhang H. Chem. Rev. 2017;117:6225–6331. - PubMed
-
- Zhao S. Kang W. Xue J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014;104:133106.
-
- Ci L. Song L. Jin C. Jariwala D. Wu D. Li Y. Srivastava A. Wang Z. F. Storr K. Balicas L. Liu F. Ajayan P. M. Nat. Mater. 2010;9:430–435. - PubMed
-
- Kuc A. Zibouche N. Heine T. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2011;83:245213.
-
- Burch K. S. Mandrus D. Park J. Nature. 2018;563:47–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

