Preparation and in vitro characterization of valsartan-loaded ethyl cellulose and poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles
- PMID: 35517152
- PMCID: PMC9058329
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra07218d
Preparation and in vitro characterization of valsartan-loaded ethyl cellulose and poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles
Abstract
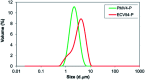
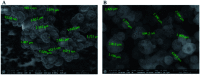
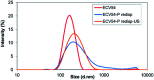
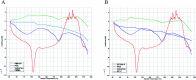
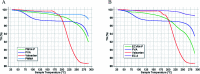
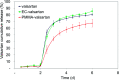
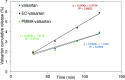
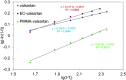
Valsartan is an antihypertensive drug used primarily orally, however, due to its hydrophobic nature it has got low bio-availability thus requiring higher dosage/frequency and causing more side effects. The aim of our work was to prepare valsartan-loaded nanoparticles by using ethyl cellulose and poly(methyl methacrylate) polymers which can be administered orally and to investigate the preparation conditions and their significance as potential drug carriers for valsartan delivery by in vitro release studies. Ethyl cellulose and poly(methyl methacrylate) polymers were used for the preparation of nanoparticles by single emulsion-solvent evaporation technique. The formation of drug-loaded nanoparticles was designed by experimental design for size and encapsulation efficiency, in addition the prepared nanosuspensions were nano spray dried in order to gain a powder form that is easy to handle and store. Both of the nano spray dried formulations had an amorphous structure in contrast to the pure drug according to differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction analysis, which can be advantageous in drug absorption. The originally processed ethyl cellulose-valsartan nanoparticles increased the solubility of the drug in the model intestinal medium, while poly(methyl methacrylate)-valsartan nanoparticles enabled substantially prolonged drug release. The release kinetics of both types of nanoparticles could be described by the Weibull model.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
In vitro characterization and invivo toxicity study of repaglinide loaded poly (methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles.Int J Pharm. 2010 Aug 30;396(1-2):194-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.06.023. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Int J Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20600729
-
Complex amorphous solid dispersions based on poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate): Study of drug release from a hydrophilic insoluble polymeric carrier in the presence and absence of a porosity increasing agent.Int J Pharm. 2019 Jul 20;566:77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.05.040. Epub 2019 May 16. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31103819
-
Oral absorption of a valsartan-loaded spray-dried emulsion based on hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose.Int J Biol Macromol. 2014 Aug;69:222-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.05.059. Epub 2014 May 28. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014. PMID: 24879921
-
Application of Central Composite Design in Optimization of Valsartan Nanosuspension to Enhance its Solubility and Stability.Curr Drug Deliv. 2016;13(1):143-57. doi: 10.2174/1567201812666150724094358. Curr Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26205900
-
Nano Spray-Dried Drugs for Oral Administration: A Review.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2021 Oct;19(7):412-441. doi: 10.1089/adt.2021.053. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2021. PMID: 34550790 Review.
Cited by
-
Sustainable Stabilizer-Free Nanoparticle Formulations of Valsartan Using Eudragit® RLPO.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 2;22(23):13069. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313069. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884873 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Rapidly Dissolving Microneedles Integrated with Valsartan-Loaded Nanoliposomes for Transdermal Drug Delivery: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 7;17(4):483. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040483. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284478 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery System and Their Role for Management of Hypertension.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(2):169-185. doi: 10.2174/0113892010291414240322112508. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38566387 Review.
References
-
- Ran R. Sun Q. Baby T. Wibowo D. Middelberg A. P. J. Zhao C. X. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017;169:78. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2017.01.008. - DOI
-
- Jong W. H. De Borm P. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008;3:133. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S596. - DOI
-
- Ding C. Li Z. Mater. Sci. Eng., C. 2017;76:1440. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.130. - DOI
-
- Crucho C. I. C. Barros M. T. Mater. Sci. Eng., C. 2017;80:771. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.06.004. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

