Cobalt ferrite supported on reduced graphene oxide as a T 2 contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 35517263
- PMCID: PMC9060952
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra09476d
Cobalt ferrite supported on reduced graphene oxide as a T 2 contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
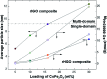
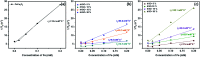
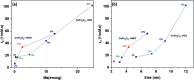
Nanoscaled spinel-structured ferrites bear promise as next-generation contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. However, the small size of the particles commonly leads to colloidal instability under physiological conditions. To circumvent this problem, supports onto which the dispersed nanoparticles can be anchored have been proposed. Amongst these, flakes of graphene have shown interesting performance but it remains unknown if and how their surface texture and chemistry affect the magnetic properties and relaxation time (T 2) of the ferrite nanoparticles. Here, it is shown that the type of graphene oxide (GO) precursor, used to make composites of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) and reduced GO, influences greatly not just the T 2 but also the average size, dispersion and magnetic behaviour of the grafted nanoparticles. Accordingly, and without compromising biocompatibility, a judicious choice of the initial GO precursor can result in the doubling of the proton relaxivity rate in this system.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures








References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

