Effective photocatalytic degradation and physical adsorption of methylene blue using cellulose/GO/TiO2 hydrogels
- PMID: 35517356
- PMCID: PMC9055038
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04509h
Effective photocatalytic degradation and physical adsorption of methylene blue using cellulose/GO/TiO2 hydrogels
Abstract
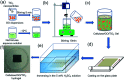
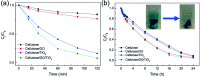
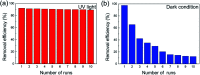
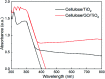
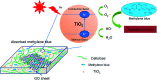
Environmentally friendly cellulose/GO/TiO2 hydrogel photocatalyst has been successfully fabricated via a green, simple, and one-step method and evaluated as the photocatalyst and adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue (MB). The XRD and FTIR analysis suggested the strong interaction among cellulose, GO and TiO2, resulting from the formation of hydrogen bonds. Due to the unique porous structure of cellulose hydrogel and introduction of GO, the cellulose/GO/TiO2 hydrogel showed superior (degradation ratio ∼ 93%) and reproducible (no significant change during the ten consecutive cycles) performance in the removal of MB under UV light. Consequently, the prepared cellulose/GO/TiO2 hydrogel can be applied as an eco-friendly, high-performance, reproducible, and stable photocatalyst and adsorbent for the removal of MB. This green hydrogel is a promising candidate for dye wastewater treatment. Moreover, this work is expected to extend the scope of bio-templated synthesis of other nanomaterials for various applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heterostructured TiO2@HKUST-1 for the enhanced removal of methylene blue by integrated adsorption and photocatalytic degradation.Environ Technol. 2021 Nov;42(26):4134-4144. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1745295. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Environ Technol. 2021. PMID: 32188338
-
Synthesis of cellulose acetate/chitosan/SWCNT/Fe3O4/TiO2 composite nanofibers for the removal of Cr(VI), As(V), Methylene blue and Congo red from aqueous solutions.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Nov 1;140:1296-1304. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.214. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31465804
-
Selective biosorption mechanism of methylene blue by a novel and reusable sugar beet pulp cellulose/sodium alginate/iron hydroxide composite hydrogel.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Oct 1;188:993-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.192. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34358601
-
Sugarcane cellulose-based composite hydrogel enhanced by g-C3N4 nanosheet for selective removal of organic dyes from water.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Apr 30;205:37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.035. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35181325
-
BiFeO3 immobilized within liquid natural rubber-based hydrogel with enhanced adsorption-photocatalytic performance.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jul 1;182:1495-1506. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.104. Epub 2021 May 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34019924
Cited by
-
Synergistic efficiency of modified banana leaf derived cellulose-g-C3N4 hybrid composite: a sustainable approach for visible-light-driven photodegradation of dyes.RSC Adv. 2025 Apr 29;15(17):13712-13727. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01156f. eCollection 2025 Apr 22. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40303559 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Biobased Membrane: Self-Entangled Cellulose Nanofibrils-ZnO-Ag Composite with High Photocatalytic Performance for Efficient Dye-Contaminated Water Treatment.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 30;9(6):7143-7153. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09062. eCollection 2024 Feb 13. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38371757 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoclay- and TiO2 Nanoparticle-Modified Poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) Hydrogels: A Multifunctional Material for Application in Photocatalytic Degradation and Adsorption-Based Removal of Organic Contaminants.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 22;7(39):35256-35268. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04595. eCollection 2022 Oct 4. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36211033 Free PMC article.
-
La-Doped ZnTiO3/TiO2 Nanocomposite Supported on Ecuadorian Diatomaceous Earth as a Highly Efficient Photocatalyst Driven by Solar Light.Molecules. 2021 Oct 15;26(20):6232. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206232. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684814 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress on Tailoring the Biomass-Derived Cellulose Hybrid Composite Photocatalysts.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 1;14(23):5244. doi: 10.3390/polym14235244. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liang X. Wang P. Li M. Zhang Q. Wang Z. Dai Y. Zhang X. Liu Y. Whangbo M.-H. Huang B. Appl. Catal., B. 2018;220:356–361. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.07.075. - DOI
-
- Zhang Y. Cui W. An W. Liu L. Liang Y. Zhu Y. Appl. Catal., B. 2018;221:36–46. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.08.076. - DOI
-
- Cunningham J., Al-Sayyed G. and Srijaranai S., in Aquatic and surface photochemistry, CRC Press, 2018, pp. 317–348
-
- He K. Chen G. Zeng G. Chen A. Huang Z. Shi J. Huang T. Peng M. Hu L. Appl. Catal., B. 2018;228:19–28. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.01.061. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

