Role of Integrin β1 in the progression and chemo-resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35517416
- PMCID: PMC9066195
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.68647
Role of Integrin β1 in the progression and chemo-resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
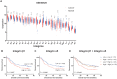
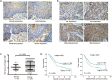
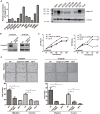
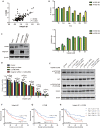
Objective: Integrins have been shown to play an important role in the tumorigenesis of many cancers. In this work, we aimed to explore the expression and clinical value of Integrin α5β1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), and the effect of integrin β1 on the development and chemo-resistance of ESCC cells. Methods: The expression profiling of integrins was analyzed in the mRNA expression dataset of ESCC. The expression of Integrin α5β1 in 278 cases of ESCC tissues and 62 cases of paracancerous tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The association between the expression of Integrin α5β1 and the survival of ESCC patients was analyzed by Kaplan-Meier analysis. The effect of Integrin β1 on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of ESCC cells was examined by MTS, Transwell migration, and Transwell invasion assay. The effect of Integrin β1 and L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM) on cisplatin resistance was detected by MTS and the signal pathways involved were analyzed by Western blotting. Results: Integrin β1 and Integrin α5 were significantly up-regulated in ESCC. High expression of Integrin β1 was also related to worse overall survival of ESCC patients and patients with low levels of both Integrin β1 and Integrin α5 showed the shortest survival. Results of IHC revealed that Integrin α5β1 was up-regulated in ESCC and its high expression was associated with poor prognosis and could serve as an independent prognostic factor. siRNA-mediated Integrin β1 silencing or antibody blocking restrained the proliferation, migration, and invasion of ESCC cells. Simultaneous knockdown of Integrin β1 and L1CAM reduced the cisplatin resistance of ESCC cells. Further studies showed that knockdown of Integrin β1 and L1CAM suppressed the activity of Akt signaling with or without cisplatin treatment. Moreover, dual high expression of Integrin β1 and L1CAM was related to worse overall survival of ESCC patients treated with preoperative chemotherapy. Conclusion: Integrin α5β1 was up-regulated in ESCC and could be used as a new prognostic indicator for ESCC patients. In addition, Integrin β1 was involved in the proliferation, invasion, and chemo-resistance of ESCC cells.
Keywords: Biomarker; Chemo-resistance; ESCC; Integrin α5β1; Prognosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A. et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:145–64. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J. et al. Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut. 2015;64:381–7. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto S, Kato K. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of esophageal cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020;20:1143–50. - PubMed
-
- Hirano H, Kato K. Systemic treatment of advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: chemotherapy, molecular-targeting therapy and immunotherapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019;49:412–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

