miR-1247-3p targets STAT5A to inhibit lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and chemotherapy resistance
- PMID: 35517418
- PMCID: PMC9066213
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.65167
miR-1247-3p targets STAT5A to inhibit lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and chemotherapy resistance
Abstract
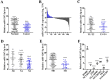
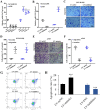
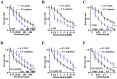
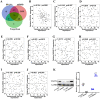
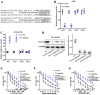
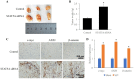
Background: Although several advancements have been achieved in research and treatment of lung adenocarcinoma in the past few years, the mechanism concerning cancerous cell migration and the cause of chemoresistance remains ambiguous. This research aimed to explore the impact of miR-1247-3p in lung adenocarcinoma. Methods: The mRNA expression of miR-1247-3p and STAT5A were conducted with qRT-PCR. Lentiviral vectors containing miR-1247-3p mimics and inhibitors were constructed. Cell migration were examined using Transwell assay. To observe chemotherapy resistance, Docetaxel, Doxorubicin, and Gefitinib were used. DIANA, miRDB, and TargetScan databases were applied to detect target genes. The binding sites were verified by double luciferase assay. Results: Low expression of miR-1247-3p was observed in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and cell lines. Its expression was lower in advanced stages. Cell migration of lung adenocarcinoma was inhibited by miR-1247-3p, and it could negatively regulate the process of chemoresistance. miR-1247-3p directly binds to 3' UTR of STAT5A mRNA, and it functions via targeting STAT5A. Conclusions: miR-1247-3p acted as a potential governor monitoring cell migration and chemotherapy resistance of LUAD by interacting with STAT5A. It has the potential to be exploited as novel therapeutic target for LUAD in the future.
Keywords: STAT5A; cell migration; chemoresistance; lung adenocarcinoma; miR-1247-3p.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-490-3p inhibits migration and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells via targeting TNKS2.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Apr 13;19(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02226-1. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33849554 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA FAM83A antisense RNA 1 (lncRNA FAM83A-AS1) targets microRNA-141-3p to regulate lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):4964-4977. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2037871. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35164653 Free PMC article.
-
The LncRNA NEAT1 Accelerates Lung Adenocarcinoma Deterioration and Binds to Mir-193a-3p as a Competitive Endogenous RNA.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):905-918. doi: 10.1159/000491958. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30036873
-
[miR-144-3p Inhibits the Invasion and Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Targeting IRS1].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021 May 20;24(5):323-330. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2021.104.05. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34034455 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
MiR-338-3p improved lung adenocarcinoma by AKAP12 suppression.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Dec 19;17(2):462-473. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.90913. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 33747281 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stemness genes and miR-1247-3p expression associate with clinicopathological parameters and prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 10;18(11):e0294171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294171. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37948380 Free PMC article.
-
CypA/TAF15/STAT5A/miR-514a-3p feedback loop drives ovarian cancer metastasis.Oncogene. 2024 Nov;43(49):3570-3585. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03188-w. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39402372
-
Role of microRNAs in regulation of doxorubicin and paclitaxel responses in lung tumor cells.Cell Div. 2023 Jul 21;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13008-023-00093-8. Cell Div. 2023. PMID: 37480054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p promotes angiogenesis in bladder cancer by targeting FOXO1.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2290033. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2023.2290033. Epub 2023 Dec 10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38073044 Free PMC article.
-
miR-1247-3p regulation of CCND1 affects chemoresistance in colorectal cancer.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 31;19(12):e0309979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309979. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39739897 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

