A Stage-Specific OTX2 Regulatory Network and Maturation-Associated Gene Programs Are Inherent Barriers to RPE Neural Competency
- PMID: 35517508
- PMCID: PMC9062105
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.875155
A Stage-Specific OTX2 Regulatory Network and Maturation-Associated Gene Programs Are Inherent Barriers to RPE Neural Competency
Abstract
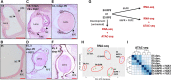
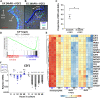
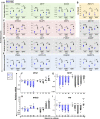
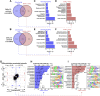
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) exhibits a diverse range of plasticity across vertebrates and is a potential source of cells for the regeneration of retinal neurons. Embryonic amniotes possess a transitory ability to regenerate neural retina through the reprogramming of RPE cells in an FGF-dependent manner. Chicken RPE can regenerate neural retina at embryonic day 4 (E4), but RPE neural competence is lost by embryonic day 5 (E5). To identify mechanisms that underlie loss of regenerative competence, we performed RNA and ATAC sequencing using E4 and E5 chicken RPE, as well as at both stages following retinectomy and FGF2 treatment. We find that genes associated with neural retina fate remain FGF2-inducible in the non-regenerative E5 RPE. Coinciding with fate restriction, RPE cells stably exit the cell cycle and dampen the expression of cell cycle progression genes normally expressed during regeneration, including E2F1. E5 RPE exhibits progressive activation of gene pathways associated with mature function independently of retinectomy or FGF2 treatment, including retinal metabolism, pigmentation synthesis, and ion transport. Moreover, the E5 RPE fails to efficiently repress OTX2 expression in response to FGF2. Predicted OTX2 binding motifs undergo robust accessibility increases in E5 RPE, many of which coincide with putative regulatory elements for genes known to facilitate RPE differentiation and maturation. Together, these results uncover widespread alterations in gene regulation that culminate in the loss of RPE neural competence and implicate OTX2 as a key determinant in solidifying the RPE fate. These results yield valuable insight to the basis of RPE lineage restriction during early development and will be of importance in understanding the varying capacities for RPE-derived retinal regeneration observed among vertebrates.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; Otx2; RPE; regeneration; reprogramming; retina.
Copyright © 2022 Tangeman, Pérez-Estrada, Van Zeeland, Liu, Danciutiu, Grajales-Esquivel, Smucker, Liang and Del Rio-Tsonis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcriptome Profiling of Embryonic Retinal Pigment Epithelium Reprogramming.Genes (Basel). 2021 May 29;12(6):840. doi: 10.3390/genes12060840. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072522 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of the chick retinal pigmented epithelium after retinal injury.BMC Biol. 2014 Apr 17;12:28. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-12-28. BMC Biol. 2014. PMID: 24742279 Free PMC article.
-
Otx2 ChIP-seq reveals unique and redundant functions in the mature mouse retina.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 18;9(2):e89110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089110. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24558479 Free PMC article.
-
The retinal pigment epithelium: Development, injury responses, and regenerative potential in mammalian and non-mammalian systems.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 Nov;85:100969. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.100969. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33901682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth factor-induced retinal regeneration in vivo.Int Rev Cytol. 1993;146:49-74. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60379-4. Int Rev Cytol. 1993. PMID: 8360013 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated single-cell multiomics uncovers foundational regulatory mechanisms of lens development and pathology.Development. 2024 Jan 1;151(1):dev202249. doi: 10.1242/dev.202249. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Development. 2024. PMID: 38180241 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic states influence chicken retinal pigment epithelium cell fate decisions.Development. 2024 Aug 1;151(15):dev202462. doi: 10.1242/dev.202462. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Development. 2024. PMID: 39120084 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lycium barbarum L. Polysaccharides on Vascular Retinopathy: An Insight Review.Molecules. 2022 Aug 31;27(17):5628. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175628. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell analyses reveal transient retinal progenitor cells in the ciliary margin of developing human retina.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 26;15(1):3567. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47933-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38670973 Free PMC article.
-
IHH enhancer variant within neighboring NHEJ1 intron causes microphthalmia anophthalmia and coloboma.NPJ Genom Med. 2023 Aug 14;8(1):22. doi: 10.1038/s41525-023-00364-x. NPJ Genom Med. 2023. PMID: 37580330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babraham Bioinformatics - FastQC (2020). A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available at: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (Accessed April 13, 2020).
-
- Benjamini Y., Yekutieli D. (2001). The Control of the False Discovery Rate in Multiple Testing under Dependency. Ann. Stat. 29, 1165–1188. 10.1214/aos/1013699998 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

