Dual-colour (near-infrared/visible) emitting annexin V for fluorescence imaging of tumour cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 35517522
- PMCID: PMC9057337
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra06495e
Dual-colour (near-infrared/visible) emitting annexin V for fluorescence imaging of tumour cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
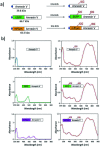
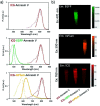
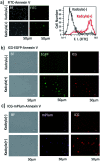
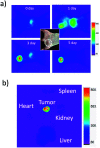
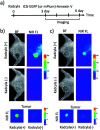
Indocyanine green (ICG) labelled recombinant annexin V proteins (ICG-EGFP-Annexin V and ICG-mPlum-Annexin V) were synthesized for dual-colour fluorescence imaging of tumour cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. The ICG-labelled fluorescent annexin V proteins showed dual (near-infrared and visible) fluorescence emissions with binding ability to phosphatidylserines on the plasma membranes of apoptotic cells. Although several types of fluorescence labelled annexin V (e.g. FITC-annexin V, Cy3- and Cy5-annexin V) have been reported, there are no dual-colour (near-infrared/visible) emitting apoptosis-detection probes which can be used in vitro and in vivo. In this paper, the utilities of the dual-colour fluorescent annexin V are demonstrated for in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging of the apoptosis of human breast tumour cells induced by an antibody-drug conjugate, Kadcyla. The results suggest that the present annexin V probes will be useful to visualize the action of anti-cancer drugs against tumours both at the cellular and whole-body level.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Kim S. Cha K. Kim I. S. Curr. Mol. Imaging. 2012;1:55–62. doi: 10.2174/2211555211201010055. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

