Applications of self-assembling ultrashort peptides in bionanotechnology
- PMID: 35517614
- PMCID: PMC9059570
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra07533f
Applications of self-assembling ultrashort peptides in bionanotechnology
Abstract
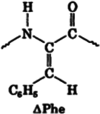
Peptides are intriguing building blocks for a variety of applications in bionanotechnology. Peptides can self-assemble into well-ordered nanostructures. Among the various nanomorphology forms, peptide nanofibers and nanotubes are relevant in biomedical applications. In this review, their applications as tissue engineering scaffolds, drug delivery vehicles, three-dimensional printing bioinks and bioimaging nanoprobes will be illustrated. This review article describes di-, tri-, tetra-peptides because they are cost-effective, simple to prepare, and amenable to production on a large scale.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bioprinting synthetic self-assembling peptide hydrogels for biomedical applications.Biomed Mater. 2015 Dec 23;11(1):014103. doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/11/1/014103. Biomed Mater. 2015. PMID: 26694103 Review.
-
Ultrashort Peptide Bioinks Support Automated Printing of Large-Scale Constructs Assuring Long-Term Survival of Printed Tissue Constructs.Nano Lett. 2021 Apr 14;21(7):2719-2729. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04426. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Nano Lett. 2021. PMID: 33492960
-
Fabrication of nanofibrous electrospun scaffolds from a heterogeneous library of co- and self-assembling peptides.Acta Biomater. 2017 Mar 15;51:268-278. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.038. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28093364
-
Peptide Bioink: Self-Assembling Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Three-Dimensional Organotypic Cultures.Nano Lett. 2015 Oct 14;15(10):6919-25. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02859. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Nano Lett. 2015. PMID: 26214046
-
Short self-assembling peptides as building blocks for modern nanodevices.Trends Biotechnol. 2012 Mar;30(3):155-65. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.11.001. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Trends Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22197260 Review.
Cited by
-
Short Peptide-Based Smart Thixotropic Hydrogels.Gels. 2022 Sep 7;8(9):569. doi: 10.3390/gels8090569. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36135280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing the ROS Sensitivity of a Responsive Supramolecular Hydrogel Using Peroxizyme Catalysis.Biomacromolecules. 2023 Jul 10;24(7):3184-3192. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00262. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Biomacromolecules. 2023. PMID: 37352147 Free PMC article.
-
Dry Two-Step Self-Assembly of Stable Supported Lipid Bilayers on Silicon Substrates.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 17;21(18):6819. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186819. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32957654 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-triggered biomimetic ultrashort peptide nanofiber hydrogels promote bone regeneration by modulating macrophage and the osteogenic immune microenvironment.Bioact Mater. 2023 Aug 14;31:231-246. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.08.008. eCollection 2024 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 37637084 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on the Rheological Properties of Single Amino Acids and Short Dipeptide Gels.Gels. 2024 Aug 1;10(8):507. doi: 10.3390/gels10080507. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39195036 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ni M. and Hauser C. A. E., Self-Assembled Peptide Nanostructures for Regenerative Medicine and Biology, in Micro and Nanofabrication Using SelfAssembled Biological Nanostructures, ed. J. C.-L. E. Svendsen, William Andrew Publishing, Oxford, 2015, Ch. 4, pp. 63–90
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

