Re-Du-Ning inhalation solution exerts suppressive effect on the secretion of inflammatory mediators via inhibiting IKKα/β/IκBα/NF-κB, MAPKs/AP-1, and TBK1/IRF3 signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 35517648
- PMCID: PMC9062024
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra00060g
Re-Du-Ning inhalation solution exerts suppressive effect on the secretion of inflammatory mediators via inhibiting IKKα/β/IκBα/NF-κB, MAPKs/AP-1, and TBK1/IRF3 signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages
Abstract
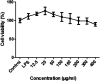
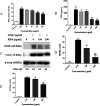
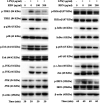
Background: Re-Du-Ning inhalation solution (RIS) is a novel preparation derived from the Re-Du-Ning injection, which has been clinically used to treat respiratory diseases such as pneumonia for more than twenty years in China. However, scant reports have been issued on its anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Aim: we investigated the suppressive effect of RIS on inflammatory mediators and explored the underlying mechanism of action. Methods: RIS freeze dried powder was characterized by HPLC analysis. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage was selected as the cell model. The cell viability was determined by using the MTT assay. Moreover, the production of nitric oxide (NO) was measured by the Griess reaction. The protein secretions from inflammatory mediators were determined by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The protein levels and enzyme activities were examined by Western blotting. The nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), AP-1, and IRF3 was further explored by immunofluorescence assay. Results: the viability of the RAW 264.7 cells was not significantly changed after 24 h incubation with RIS concentration up to 400 μg mL-1. The RIS remarkably reduced the production of NO and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and downregulated the expression of iNOS and COX-2. The concentrations of cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) and chemokines (MCP-1, CCL-5, and MIP-1α) in the culture medium were significantly decreased by the RIS treatment. Furthermore, the phosphorylation of IκB-α, IKKα/β, TBK1, ERK, p38, JNK, NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 was downregulated by the RIS treatment. The nuclear translocation of NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 was also inhibited after the RIS treatment. Conclusion: the suppressive effect of RIS is associated with the regulated NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 and their upstream proteins. This study provides a pharmacological basis for the application of RIS in the treatment of inflammatory disorders.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Xiao Qing Long Tang essential oil exhibits inhibitory effects on the release of pro-inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 signalling in the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.RSC Adv. 2019 Apr 26;9(23):12977-12989. doi: 10.1039/c9ra01448a. eCollection 2019 Apr 25. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35520778 Free PMC article.
-
Dingchuan tang essential oil inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators via suppressing the IRAK/NF-κB, IRAK/AP-1, and TBK1/IRF3 pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Sep 4;12:2731-2748. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S160645. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30233137 Free PMC article.
-
Schisandra Chinensis Lignans Suppresses the Production of Inflammatory Mediators Regulated by NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells.Molecules. 2018 Dec 14;23(12):3319. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123319. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30558163 Free PMC article.
-
An ethanolic extract of the aerial part of Siegesbeckia orientalis L. inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators regulated by AP-1, NF-κB and IRF3 in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells.Biosci Trends. 2018;12(3):330-337. doi: 10.5582/bst.2018.01103. Biosci Trends. 2018. PMID: 30012916
-
Sichen Formula Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Blocking the TLR4 Signaling Pathways.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Feb 2;17:297-312. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S372981. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 36756190 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Combating the Coronavirus Pandemic: Early Detection, Medical Treatment, and a Concerted Effort by the Global Community.Research (Wash D C). 2020 Jun 16;2020:6925296. doi: 10.34133/2020/6925296. eCollection 2020. Research (Wash D C). 2020. PMID: 32607499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Folic acid-conjugated magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with quercetin: a theranostic approach for cancer management.RSC Adv. 2020 Jun 17;10(39):23148-23164. doi: 10.1039/d0ra00664e. eCollection 2020 Jun 16. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35520307 Free PMC article.
-
Edgeworthia gardneri (Wall.) Meisn. Water Extract Ameliorates Palmitate Induced Insulin Resistance by Regulating IRS1/GSK3β/FoxO1 Signaling Pathway in Human HepG2 Hepatocytes.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 30;10:1666. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01666. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32082162 Free PMC article.
-
Octominin Inhibits LPS-Induced Chemokine and Pro-inflammatory Cytokine Secretion from RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Blocking TLRs/NF-κB Signal Transduction.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 27;10(4):511. doi: 10.3390/biom10040511. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32230927 Free PMC article.
-
Xiao Qing Long Tang essential oil exhibits inhibitory effects on the release of pro-inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB, AP-1, and IRF3 signalling in the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.RSC Adv. 2019 Apr 26;9(23):12977-12989. doi: 10.1039/c9ra01448a. eCollection 2019 Apr 25. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35520778 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

