Restoration of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Activity Functions as a Pivotal Therapeutic Target of Anti-Glutamate-Induced Excitotoxicity to Attenuate Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Depletion
- PMID: 35517826
- PMCID: PMC9065279
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.877175
Restoration of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Activity Functions as a Pivotal Therapeutic Target of Anti-Glutamate-Induced Excitotoxicity to Attenuate Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Depletion
Abstract
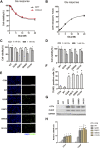
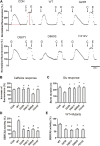
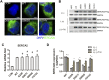
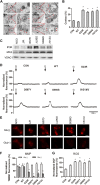
Glutamate-induced excitotoxicity is a pathological basis of many acute/chronic neurodegenerative diseases. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA2b) is a membrane-embedded P-type ATPase pump that manages the translocation of calcium ions (Ca2+) from cytosol into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) calcium stores. It participates in a wide range of biological functions in the central nervous system (CNS). However, the role of SERCA2b in glutamate-induced excitotoxicity and its mechanism must be elucidated. Herein, we demonstrate that SERCA2b mutants exacerbate the excitotoxicity of hypo-glutamate stimulation on HT22 cells. In this study, SERCA2b mutants accelerated Ca2+ depletion through loss-of-function (reduced pumping capacity) or gain-of-function (acquired leakage), resulting in ER stress. In addition, the occurrence of ER Ca2+ depletion increased mitochondria-associated membrane formation, which led to mitochondrial Ca2+ overload and dysfunction. Moreover, the enhancement of SERCA2b pumping capacity or inhibition of Ca2+ leakage attenuated Ca2+ depletion and impeded excitotoxicity in response to hypo-glutamate stimulation. In conclusion, SERCA2b mutants exacerbate ER Ca2+-depletion-mediated excitotoxicity in glutamate-sensitive HT22 cells. The mechanism of disruption is mainly related to the heterogeneity of SERCA2b mutation sites. Stabilization of SRECA2b function is a critical therapeutic approach against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. These data will expand understanding of organelle regulatory networks and facilitate the discovery and creation of drugs against excitatory/inhibitory imbalance in the CNS.
Keywords: CDN1163; SERCA2b; calcium depletion; endoplasmic reticulum stress; excitotoxicity; mitochondria.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Ye, Pang, Kessi, Xiong, Chen, Peng, Yang and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox protein 1 (Pdx-1) maintains endoplasmic reticulum calcium levels through transcriptional regulation of sarco-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2b (SERCA2b) in the islet β cell.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 21;289(47):32798-810. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.575191. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25271154 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase limits Ca2+ accumulation in the endoplasmic reticulum by inhibiting the Ca2+ pump SERCA2b.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100310. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100310. Epub 2021 Jan 19. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33482198 Free PMC article.
-
Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ -ATPase (SERCA2b) mediates oxidation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress to regulate neuropathic pain.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 May;179(9):2016-2036. doi: 10.1111/bph.15744. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34811737
-
Structural basis of the conformational and functional regulation of human SERCA2b, the ubiquitous endoplasmic reticulum calcium pump.Bioessays. 2022 Jul;44(7):e2200052. doi: 10.1002/bies.202200052. Epub 2022 May 13. Bioessays. 2022. PMID: 35560336 Review.
-
Sarco-Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Release Model Based on Changes in the Luminal Calcium Content.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1131:337-370. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12457-1_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31646517 Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium regulation by SERC-A before and during Alzheimer disease.Biomedica. 2023 Mar 30;43(1):51-60. doi: 10.7705/biomedica.6704. Biomedica. 2023. PMID: 37167461 Free PMC article. English, Spanish.
-
Xingnaojing injection alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in Vivo and in Vitro.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 24;10(3):e25267. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25267. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38327400 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse event profile of memantine and donepezil combination therapy: a real-world pharmacovigilance analysis based on FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) data from 2004 to 2023.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1439115. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1439115. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39101151 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases-an update.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May 19. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01576-w. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40389567 Review.
References
-
- Angelova P. R., Vinogradova D., Neganova M. E., Serkova T. P., Sokolov V. V., Bachurin S. O., et al. (2019). Pharmacological Sequestration of Mitochondrial Calcium Uptake Protects Neurons against Glutamate Excitotoxicity. Mol. Neurobiol. 56 (3), 2244–2255. 10.1007/s12035-018-1204-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

