Trimethyl-Chitosan Coated Gold Nanoparticles Enhance Delivery, Cellular Uptake and Gene Silencing Effect of EGFR-siRNA in Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35517864
- PMCID: PMC9065351
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.871541
Trimethyl-Chitosan Coated Gold Nanoparticles Enhance Delivery, Cellular Uptake and Gene Silencing Effect of EGFR-siRNA in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
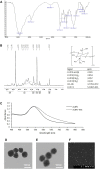
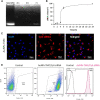
Purpose: Despite the promising therapeutic effects of gene silencing with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), the challenges associated with delivery of siRNAs to the tumor cells in vivo, has greatly limited its clinical application. To overcome these challenges, we employed gold nanoparticles modified with trimethyl chitosan (TMC) as an effective delivery carrier to improve the stability and cellular uptake of siRNAs against epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that is implicated in breast cancer. Methods: AuNPs were prepared by the simple aqueous reduction of chloroauric acid (HAuCl4) with ascorbic acid and coated with synthesized TMC. EGFR-siRNA was then complexed with the AuNPs-TMC via electrostatic interaction to make AuNPs-TMC/EGFR-siRNA with a w/w ratio of 10:1. Nanoparticles were assessed for physicochemical characteristics and in vitro cellular behavior on MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Results: Spherical and positively charged AuNPs-TMC (67 nm, +45 mV) were successfully complexed with EGFR-siRNA (82 nm, +11 mV) which were able to retard the gene migration completely. Confocal microscopy and flow cytometry analysis demonstrated complete cellular uptake of Cy5 labeled AuNPs-TMC in the MCF-7 cells after 4 h incubation. MTT test after 48 h incubation showed that the AuNPs-TMC were safe but when combined with EGFR-siRNA exert significant cytotoxicity while the cell viability was about 50%. These nanocomplexes also showed a high gene expression knockdown (86%) of EGFR and also a high apoptosis rate (Q2 + Q3 = 18.5%) after 24 h incubation. Conclusion: This study suggests that the simply synthesized AuNPs-TMC are novel, effective, and promising nanocarriers for siRNA delivery, and AuNPs-TMC/EGFR-siRNA appears to be a potential therapeutic agent for breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: EGFR-siRNA; breast cancer; gold nanoparticles (AuNPs); siRNA delivery; trimethyl chitosan (TMC).
Copyright © 2022 Baghani, Noroozi Heris, Khonsari, Dinarvand, Dinarvand and Atyabi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Atyabi F., Majzoob S., Iman M., Salehi M., Dorkoosh F. (2005). In Vitro evaluation and Modification of Pectinate Gel Beads Containing Trimethyl Chitosan, as a Multi-Particulate System for Delivery of Water-Soluble Macromolecules to colon. Carbohydr. Polym. 61, 39–51. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.02.005 - DOI
-
- Boca S. C., Potara M., Toderas F., Stephan O., Baldeck P. L., Astilean S. (2011). Uptake and Biological Effects of Chitosan-Capped Gold Nanoparticles on Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 31, 184–189. 10.1016/j.msec.2010.08.015 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

