Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery through Vesicles and Particles: Preparation and Applications
- PMID: 35517881
- PMCID: PMC9012920
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2022.006
Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery through Vesicles and Particles: Preparation and Applications
Abstract
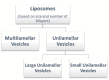
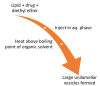
Transdermal delivery over the past decade has become the field of interest for drug delivery due to its various advantages such as no first-pass metabolism, increased drug bioavailability, and easy administration. Different vesicle systems like ethosomes, liposomes, niosomes, and transferosomes along with particle systems like lipid nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes have been developed. These vesicles and particle systems have been developed using various easy and effective methods like cold injection method, rotary film evaporation, thin film hydration, high shear homogenization, solvent extraction method, and many more. These drug delivery systems are a very effective and feasible option for transdermal drug delivery and further developments can be made to increase their use. This article explains in detail the preparation methods and applications for these drug delivery systems.
Keywords: Dermal; Drug delivery; Ethosomes; Nanoparticles; Niosomes; Particle systems; Transdermal; Transferosomes; Vesicle systems.
©2022 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of Statistical Tooling Techniques for Designing of Carvedilol Nanolipid Transferosomes and its Dermatopharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Studies.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020;8(6):452-470. doi: 10.2174/2211738508666200928164820. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32988361
-
Advanced Drug Delivery Systems for Transdermal Delivery of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: A Review.Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(8):1087-1099. doi: 10.2174/1567201815666180605114131. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 29875000 Review.
-
Transferosomes as a transdermal drug delivery system: Dermal kinetics and recent developments.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024 Jan-Feb;16(1):e1918. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1918. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37527953 Review.
-
Niosomes: a controlled and novel drug delivery system.Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(7):945-53. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.945. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011. PMID: 21719996 Review.
-
Methods for preparation of niosomes: A focus on thin-film hydration method.Methods. 2022 Mar;199:9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.05.004. Epub 2021 May 14. Methods. 2022. PMID: 34000392
Cited by
-
Formulation and Characterization of Ethosomes for Transdermal Delivery of Prinsepia Utilis Rogle Seed Oil with Ameliorative Effects against UVB-Induced Skin Damage.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 May 30;25(5):122. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02822-w. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38816546
-
Microneedle-Assisted Transfersomes as a Transdermal Delivery System for Aspirin.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 29;16(1):57. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010057. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38258069 Free PMC article.
-
Translation from Preclinical Research to Clinical Trials: Transdermal Drug Delivery for Neurodegenerative and Mental Disorders.Pharm Res. 2024 Jun;41(6):1045-1092. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03718-x. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38862719 Review.
-
Nanovesicles and Human Skin Interaction: A Comparative Ex-Vivo Study.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jun 16;15(12):937. doi: 10.3390/nano15120937. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40559300 Free PMC article.
-
Niacinamide: a review on dermal delivery strategies and clinical evidence.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Dec;14(12):3512-3548. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01593-y. Epub 2024 May 9. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38722460 Review.
References
-
- Venus M, Waterman J, McNab I. Basic physiology of the skin. Surgery (Oxford) 2010;28(10):469–72. doi: 10.1016/j.mpsur.2010.07.011. - DOI
-
- Malvey S, Rao JV, Arumugam KM. Transdermal drug delivery system: a mini review. Pharma Innov J. 2019;8(1):181–97.
-
- Ng KW, Lau WM. Skin deep: the basics of human skin structure and drug penetration. In: Dragicevic N, Maibach HI, eds. Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Chemical Methods in Penetration Enhancement. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2015. p. 3-11. 10.1007/978-3-662-45013-0_1 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous