Protective Role of trans-Chalcone against the Progression from Simple Steatosis to Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Regulation of miR-122, 21, 34a, and 451
- PMID: 35517895
- PMCID: PMC9012929
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2022.022
Protective Role of trans-Chalcone against the Progression from Simple Steatosis to Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Regulation of miR-122, 21, 34a, and 451
Abstract
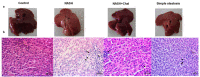
Purpose: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an inflammatory disorder and an aggressive form of fatty liver disease. Certain microRNAs, including miR-122, 21, 34a, and 451, are involved in the transition from steatosis to NASH. This study examined how trans-chalcone (the core of chalcone derivatives) affects NAFLD progression by regulating miRNAs. Methods: Male rats were divided into three groups (n = 7/group) as follows: control, rats were gavaged with 10% tween 80 (for two weeks); NASH, rats were gavaged with a high-fat liquid diet (HFD; for six weeks) and 10% tween 80 (for two weeks); NASH + Chal, rats were gavaged with the HFD (for six weeks) and trans-chalcone (for two weeks). Hepatic expression levels of miR-122, 21, 34a, and 451 were determined. Results: trans-Chalcone reversed histological abnormalities, reduced liver injury markers, and attenuated insulin resistance in HFD-fed rats. In the liver, HFD-induced NASH increased the expression level of miR-34a and decreased expression levels of miR-122, 21, and 451. However, trans-chalcone inhibited HFD-induced changes in expression levels of these miRNAs. Conclusion: trans-Chalcone could inhibit the transition from steatosis to NASH through the modulation of miR-122, 21, 34a, and 451 expression levels in the liver.
Keywords: Liver; Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; Rat; miRNAs; trans-Chalcone.
©2022 The Authors.
Similar articles
-
trans-Chalcone prevents insulin resistance and hepatic inflammation and also promotes hepatic cholesterol efflux in high-fat diet-fed rats: modulation of miR-34a-, miR-451-, and miR-33a-related pathways.Food Funct. 2018 Aug 15;9(8):4292-4298. doi: 10.1039/c8fo00923f. Food Funct. 2018. PMID: 30039136
-
Preventive effect of trans-chalcone on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Improvement of hepatic lipid metabolism.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:1306-1312. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.196. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551380
-
Protective Effect of Trans-chalcone Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation Is Associated with Changes in miR-146a And pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Expression in Male Rats.Inflammation. 2019 Dec;42(6):2048-2055. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01067-1. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31473901
-
Role of microRNA in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a comprehensive review.J Int Med Res. 2023 Sep;51(9):3000605231197058. doi: 10.1177/03000605231197058. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37676968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comparison of the Gene Expression Profiles of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease between Animal Models of a High-Fat Diet and Methionine-Choline-Deficient Diet.Molecules. 2022 Jan 27;27(3):858. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030858. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatoprotective and antifibrotic effects of trans-chalcone against bile duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis in rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(10):1194-1201. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68342.15040. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37736516 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-34a Mediates High-Fat-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance by Targeting ENO3.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 31;15(21):4616. doi: 10.3390/nu15214616. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960269 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Circular RNA Homeodomain Interacting Protein Kinase 3 and Circular RNA 0046367 through Wnt/Beta-Catenin Pathway on the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Egyptian Patients.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Jan;11(4):614-625. doi: 10.52547/rbmb.11.4.614. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37131898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asghari S, Rafraf M, Farzin L, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Ghavami SM, Somi MH. Effects of pharmacologic dose of resveratrol supplementation on oxidative/antioxidative status biomarkers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Adv Pharm Bull. 2018;8(2):307–17. doi: 10.15171/apb.2018.036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources