Selective expansion of regulatory T cells by NKTR-358 in healthy volunteers and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 35517914
- PMCID: PMC9062472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2022.100152
Selective expansion of regulatory T cells by NKTR-358 in healthy volunteers and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate NKTR-358, a polyethylene glycol-interleukin-2 conjugate composition designed to selectively induce regulatory T cells (Tregs), in first-in-human studies.
Methods: Healthy volunteers and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) received single- or multiple-dose (biweekly) NKTR-358 or placebo in two sequential, randomized, phase 1 studies (single ascending dose [SAD; NCT04133116] and multiple ascending dose [MAD; NCT03556007]). Primary objectives were safety and tolerability; secondary objectives included pharmacokinetics (PK) and immune effects of NKTR-358; exploratory objectives included effects on SLE disease activity.
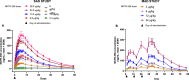
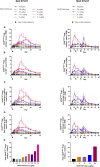
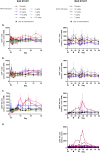
Results: There were eight ascending dose cohorts in the SAD study (0.3-28.0 μg/kg: n = 76; placebo: n = 24) and four in the MAD study (3-24.0 μg/kg: n = 36; placebo: n = 12). Most adverse events (AEs) were grade 1-2 injection-site reactions, with no treatment-related serious or severe AEs, or deaths. PK data showed dose proportionality and prolonged exposure (mean half-life: 7.4-12.9 days). Dose-dependent, selective, and sustained increases in percentages and absolute numbers of total CD4+ Tregs and CD25bright Tregs were observed, with no significant changes in conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and low-level increases in natural killer cells. At the highest doses tested, administration of NKTR-358 resulted in a 12-17-fold increase in CD25bright Tregs over baseline that was sustained for 20-30 days.
Conclusion: NKTR-358 was well tolerated, had a suitable PK profile for biweekly dosing, and led to marked and selective dose-dependent increases in CD25bright Tregs, with no significant changes in conventional T cells. These results provide strong support for further testing in SLE and other inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Autoimmune disease; IL-2 receptor; Interleukin-2; Regulatory T cells; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: CF, RF, VC, RL, ID, ND, CH, JG, NH, JZ and BK report financial support was provided by Nektar Therapeutics. CF reports a relationship with Nektar Therapeutics that includes: employment and equity or stocks. RF reports a relationship with Nektar Therapeutics that includes: consulting or advisory. RF reports a relationship with Genentech/Roche that incudes personal fees and grants. RF reports a relationship with AstraZeneca that includes: consulting or advisory. RF reports a relationship with Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals that includes: consulting or advisory. VC reports a relationship with AbbVie Inc that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Amgen Inc that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Boehringer Ingelheim Corp USA that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Boston Pharmaceuticals that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Eli Lilly and Company that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with EMD Serono Inc that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Genentech that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with GlaxoSmithKline USA that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Merck & Co Inc that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Nektar Therapeutics that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Novartis that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Pfizer that includes: funding grants. VC reports a relationship with Roche that includes: funding grants. VC reports that Pinnacle Research Group/Anniston Medical Clinic also received funding from Astellas Pharma Global Development Inc. RL reports a relationship with Gilead Sciences Inc that includes: consulting or advisory. RL reports a relationship with Exagen Inc that includes: consulting or advisory. RL reports a relationship with Myriad Genetics Inc that includes: consulting or advisory. RL reports a relationship with Sanofi that includes: paid expert testimony and speaking and lecture fees. RL reports a relationship with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc that includes: paid expert testimony and speaking and lecture fees. RL reports a relationship with Bristol Myers Squibb Co that includes: paid expert testimony and speaking and lecture fees. RL reports a relationship with AbbVie that includes: paid expert testimony and speaking and lecture fees. ND reports a relationship with Nektar Therapeutics that includes: employment and equity or stocks. CH reports a relationship with Nektar Therapeutics that includes: employment and equity or stocks. JG reports a relationship with Nektar Therapeutics that includes: employment and equity or stocks. NH reports a relationship with GlaxoSmithKline that includes: employment. DD reports a relationship with PRA Health Sciences that includes: employment. DD reports a relationship with ICON plc that includes: employment. JZ reports a relationship with Nektar Therapeutics that includes: employment and equity or stocks. BK reports a relationship with Nektar Therapeutics that includes: employment and equity or stocks. ID has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Phase 1, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single- and multiple-dose escalation study to evaluate the safety and pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of PF-06835375, a C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5 directed antibody, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Jun 6;26(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03337-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38845046 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
NKTR-358: A novel regulatory T-cell stimulator that selectively stimulates expansion and suppressive function of regulatory T cells for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.J Transl Autoimmun. 2021 May 6;4:100103. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100103. eCollection 2021. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 34041473 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of PF-06823859, an Anti-Interferon β Monoclonal Antibody: A Randomized, Phase I, Single- and Multiple-Ascending-Dose Study.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021 Mar;10(3):307-316. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.887. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021. PMID: 33352008 Clinical Trial.
-
The Regulatory T Cell in Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 18;10:159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00159. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30833946 Free PMC article.
-
The Proportion of Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis.J Immunol Res. 2018 Sep 3;2018:7103219. doi: 10.1155/2018/7103219. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30255107 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Protein- and Peptide-Based Chemical Conjugates: Past, Present, and Future.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 10;15(2):600. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020600. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequential immunotherapy: towards cures for autoimmunity.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Jul;23(7):501-524. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-00959-8. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38839912 Review.
-
A humanized IL-2 mutein expands Tregs and prolongs transplant survival in preclinical models.J Clin Invest. 2024 Mar 1;134(5):e173107. doi: 10.1172/JCI173107. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38426492 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose interleukin-2 therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus.Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2023 Sep 27;4(3):150-156. doi: 10.2478/rir-2023-0021. eCollection 2023 Sep. Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 37781677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune cell aberrations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: navigating the targeted therapies toward precision management.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jun 16;30(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00749-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40524185 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- von Spee-Mayer C., Siegert E., Abdirama D., Rose A., Klaus A., Alexander T., Enghard P., Sawitzki B., Hiepe F., Radbruch A., Burmester G.-R., Riemekasten G., Humrich J.Y. Low-dose interleukin-2 selectively corrects regulatory T cell defects in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016;75:1407–1415. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207776. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

