Notoginsenoside Fe suppresses diet induced obesity and activates paraventricular hypothalamic neurons
- PMID: 35518019
- PMCID: PMC9059641
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra07842d
Notoginsenoside Fe suppresses diet induced obesity and activates paraventricular hypothalamic neurons
Abstract
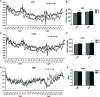
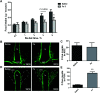
Obesity has become a major public health challenge worldwide. Energy imbalance between calorie acquisition and consumption is the fundamental cause of obesity. Notoginsenoside Fe is a naturally occurring compound in Panax notoginseng, a herb used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases in traditional Chinese medicine. Here, we evaluated the effect of notoginsenoside Fe on obesity development induced by high-fat diet in C57BL/6 mice. Our results demonstrated that notoginsenoside Fe decreased food intake and body weight, as well as protected liver structure integrity and normal function. Metabolic cage analysis showed that notoginsenoside Fe also promoted resting metabolic rate. In addition, intracerebroventricular (i.c.v) injection of notoginsenoside Fe induced C-Fos expression in the paraventricular nucleus (PVH) but not the arcuate nucleus (ARC) of the hypothalamus. These results suggest that Fe may reduce body weight through the activation of energy-sensing neurons in the hypothalamus.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they are no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Knight J. A. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2011;41:107–121. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

