Insight into the effect of quinic acid on biofilm formed by Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 35518066
- PMCID: PMC9060517
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra09136f
Insight into the effect of quinic acid on biofilm formed by Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
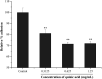
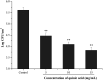
The biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus on food contact surfaces is the main risk of food contamination. In the present study, we firstly investigated the inhibitory effect of quinic acid (QA) on biofilm formed by S. aureus. Crystal violet staining assay and microscopy analysis clearly showed that QA at sub-MIC concentrations was able to significantly reduce the biofilm biomass and cause a collapse on biofilm architecture. Meanwhile, fibrinogen binding assay showed that QA had obviously effect on the S. aureus bacteria adhesion. XTT reduction assay and confocal laser scanning microscopic images revealed that QA significantly decreased metabolic activity and viability of biofilm cells. In addition, qRT-PCR analysis explored the potential inhibitory mechanism of QA against biofilm formation, which indicated that QA significantly repressed the gene sarA and activated the gene agrA. Moreover, QA exhibited a highly ability to reduce the number of sessile S. aureus cells adhered on the stainless steel. So, it was suggested that QA could be used as a promising antibiofilm agent to control biofilm formation of S. aureus.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibitory Effect of 2R,3R-Dihydromyricetin on Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus aureus.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2018 Aug;15(8):475-480. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2017.2405. Epub 2018 May 30. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2018. PMID: 29847738
-
Inhibitory effect of a natural phenolic compound, 3-p-trans-coumaroyl-2-hydroxyquinic acid against the attachment phase of biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus through targeting sortase A.RSC Adv. 2019 Oct 11;9(56):32453-32461. doi: 10.1039/c9ra05883d. eCollection 2019 Oct 10. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35529766 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol Inhibits the Primary Attachment Phase of Biofilm Formation in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2017 Nov 15;8:2263. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02263. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29187848 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus aureus on Various Surfaces and Their Resistance to Chlorine Sanitizer.J Food Sci. 2015 Oct;80(10):M2279-86. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13017. Epub 2015 Sep 28. J Food Sci. 2015. PMID: 26417663
-
Inhibitory Effects of Lactobionic Acid on Biofilm Formation and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus.Foods. 2024 Aug 31;13(17):2781. doi: 10.3390/foods13172781. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39272546 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Antimicrobial Peptide Octopromycin Suppresses Biofilm Formation and Quorum Sensing in Acinetobacter baumannii.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 21;12(3):623. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030623. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978490 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Campylobacter jejuni Biofilm Formation by D-Amino Acids.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Nov 23;9(11):836. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9110836. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33238583 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of Thermophilic Bacteria Geobacillus subterraneus From Mount Tangkuban Perahu and the Novelty as a Candidate for Streptococcus mutans Anti-Biofilm.Int J Dent. 2024 Nov 25;2024:4285984. doi: 10.1155/ijod/4285984. eCollection 2024. Int J Dent. 2024. PMID: 39629160 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Possible Ways to Enhance the Potential and Use of Natural Products through Nanotechnology in the Battle against Biofilms of Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens.Pathogens. 2023 Feb 7;12(2):270. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12020270. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36839543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of kaffir lime essential oils and their active constituents against Staphylococcus aureus focusing on sortase A.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 18;11(2):e41977. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41977. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40013263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu M. H. Wu X. X. Li J. K. Liu L. Zhang R. G. Shao D. Y. Du X. D. Food Control. 2017;73:613–618. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.09.015. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

