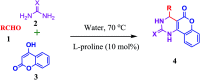An efficient, mild and metal free l-proline catalyzed construction of fused pyrimidines under microwave conditions in water
- PMID: 35518091
- PMCID: PMC9060310
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra07517d
An efficient, mild and metal free l-proline catalyzed construction of fused pyrimidines under microwave conditions in water
Abstract
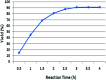
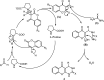
One-pot condensation of 4-hydroxy coumarins, aldehydes and urea/thiourea to build C-C and C-N bonds is described. Fused pyrimidines have been synthesized under mild reaction conditions using l-proline. The protocol has been performed rapidly and efficiently in water under metal free conditions. Heterocyclic derivatives have been synthesized using the present methodology and avoid the use of hazardous solvents over conventional organic solvents. A proposed mechanism could be established for three component reactions. The present study reveals the first case in which l-proline has been explored as a homogeneous catalyst in the synthesis of fused pyrimidines in water under microwave irradiation. This synthesis involves simple workup and acceptable efficiency. The most notable feature of this protocol is the ability of the catalyst to influence asymmetric induction in the reaction.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metal-Free Construction of Fused Pyrimidines via Consecutive C-C and C-N Bond Formation in Water.ACS Omega. 2018 Nov 7;3(11):15035-15042. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01993. eCollection 2018 Nov 30. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 31458170 Free PMC article.
-
One-pot facile and mild construction of densely functionalized pyrimidines in water via consecutive C-C and C-S bonds formation.RSC Adv. 2018 Oct 3;8(59):33952-33959. doi: 10.1039/c8ra04363a. eCollection 2018 Sep 28. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35548808 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis of Fused Chromeno-pyrazolo-phthalazine Derivatives with Silicasupported Bismuth Nitrate under Solvent-free Conditions.Curr Org Synth. 2021;18(8):854-861. doi: 10.2174/1570179417666201208112520. Curr Org Synth. 2021. PMID: 33292122
-
L-Proline: A Versatile Organo-Catalyst in Organic Chemistry.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(6):1108-1140. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220720105845. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 35864793 Review.
-
Diversity Oriented Synthesis of 4H-Pyrimido[2,1-b]benzothiazole Derivatives via Biginellis Reaction: A Review.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2018;21(4):236-253. doi: 10.2174/1386207321666180330170456. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2018. PMID: 29611485 Review.
Cited by
-
Amino acid-based deep eutectic solvent as a versatile catalyst for the green synthesis of chromenopyrimidines.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 22;15(1):26584. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08820-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40695859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hajinasiri R. Hossaini Z. Sheikholeslami-Farahani F. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2015;18:42. doi: 10.2174/1386207317666141203123133. - DOI - PubMed
- Hossaini Z. Soltani S. Sheikholeslami-Farahani F. Sayyed-Alangi S. Z. Sajjadi-Ghotabadi H. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2015;51:26. doi: 10.1007/s10593-015-1654-0. - DOI
- Hossaini Z. Rostami-Charati F. Ghasemian M. Afshari Sharif Abad S. Synlett. 2015;26:1222. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1380504. - DOI
-
- Heijden V. D. G. Ruijter E. Orru R. V. A. Synlett. 2013:666.
- Hulme C., Ayaz M., Martinez-Ariza G., Medda F. and Shaw A., in Small molecule medicinal chemistry: strategies and technologies, ed. W. Czechtizky and P. Hamley, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2015, ch. 6
- Gollner A. Synlett. 2015:426. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1379947. - DOI
-
- Balalaie S. Bararjanian M. Amani A. M. Movassagh B. Synlett. 2006:263. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-926227. - DOI
- Kotrusz P. Toma S. ARKIVOC. 2006;v:100.
- Mabry J. Ganem B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006;47:55. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.10.124. - DOI
- Chandrasekher S. Vijeender K. Reddy V. K. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005;46:6991. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.08.066. - DOI
- Chandrasekhar S. Narsihmulu C. Reddy N. R. K. Sultana S. S. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004;45:4581. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2004.03.116. - DOI
- Darbre T. Machuqueiro M. Chem. Commun. 2003:1090. doi: 10.1039/B301117H. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources