Population pharmacokinetic model and limited sampling strategy for clozapine using plasma and dried blood spot samples
- PMID: 35518123
- PMCID: PMC9066631
- DOI: 10.1177/20451253211065857
Population pharmacokinetic model and limited sampling strategy for clozapine using plasma and dried blood spot samples
Abstract
Background: To improve efficacy, therapeutic drug monitoring is often used in clozapine therapy. Trough level monitoring is regular, but trough levels provide limited information about the pharmacokinetics of clozapine and exposure in time. The area under the concentration time curve (AUC) is generally valued as better marker of drug exposure in time but calculating AUC needs multiple sampling. An alternative approach is a limited sampling scheme in combination with a population pharmacokinetic model meant for Bayesian forecasting. Furthermore, multiple venepunctions can be a burden for the patient, whereas collecting samples by means of dried blood spot (DBS) sampling can facilitate AUC-monitoring, making it more patient friendly.
Objective: Development of a population pharmacokinetic model and limited sampling strategy for estimating AUC0-12h (a twice-daily dosage regimen) and AUC0-24h (a once-daily dosage regimen) of clozapine, using a combination of results from venepunctions and DBS sampling.
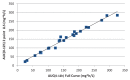
Method: From 15 schizophrenia patients, plasma and DBS samples were obtained before administration and 2, 4, 6, and 8 h after clozapine intake. MwPharm® pharmacokinetic software was used to parameterize a population pharmacokinetic model and calculate limited sampling schemes.
Results: A three-point sampling strategy with samples at 2, 6, and 8 h after clozapine intake gave the best estimation of the clozapine AUC0-12h and at 4, 10, and 11 h for the AUC0-24h. For clinical practice, however, a two-point sampling strategy with sampling points at 2 and 6 h was sufficient to estimate AUC0-12h and at 4 and 11 h for AUC0-24h.
Conclusion: A pharmacokinetic model with a two-time point limited sampling strategy meant for Bayesian forecasting using DBS sampling gives a better prediction of the clozapine exposure in time, expressed as AUC, compared to trough level monitoring. This limited sampling strategy might therefore provide a more accurate prediction of effectiveness and occurrence of side effects compared to trough level monitoring. The use of DBS samples also makes the collection of clozapine samples easier and wider applicable.
Keywords: clozapine; dried blood spot; limited sampling strategy; pharmacokinetics; population pharmacokinetic model; therapeutic drug monitoring.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Easy-to-use, accurate and flexible individualized Bayesian limited sampling method without fixed time points for ciclosporin monitoring after liver transplantation.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Mar 1;21(5):549-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02364.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15740538
-
Flexible limited sampling model for monitoring tacrolimus in stable patients having undergone liver transplantation with samples 4 to 6 hours after dosing is superior to trough concentration.Ther Drug Monit. 2008 Aug;30(4):456-61. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0b013e31818162b9. Ther Drug Monit. 2008. PMID: 18641539
-
Population pharmacokinetics of ciclosporin in haematopoietic allogeneic stem cell transplantation with emphasis on limited sampling strategy.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;73(4):553-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04116.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21988410 Free PMC article.
-
Mycophenolate, clinical pharmacokinetics, formulations, and methods for assessing drug exposure.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2011 Apr;25(2):47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2011. PMID: 21190834
-
How accurate and precise are limited sampling strategies in estimating exposure to mycophenolic acid in people with autoimmune disease?Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014 Mar;53(3):227-245. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0124-z. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014. PMID: 24327238 Review.
References
-
- Azorin JM, Spiegel R, Remington G, et al. A double-blind comparative study of clozapine and risperidone in the management of severe chronic schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2001; 158: 1305–1313. - PubMed
-
- Conley RR, Tamminga CA, Kelly DL, et al. Treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients respond to clozapine after olanzapine non-response. Biol Psychiatry 1999; 46: 73–77. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi H, Powell V, Geisler S, et al. Clozapine administration in clinical practice: once-daily versus divided dosing. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2016; 134: 234–240. - PubMed
-
- Khan AY, Preskorn SH. Examining concentration-dependent toxicity of clozapine: role of therapeutic drug monitoring. J Psychiatr Pract 2005; 11: 289–301. - PubMed
-
- Hiemke C, Baumann P, Bergemann N, et al. AGNP consensus guidelines for therapeutic drug monitoring in psychiatry: update 2011. Pharmacopsychiatry 2011; 44: 195–235. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

