Novel MoS2 quantum dots as a highly efficient visible-light driven photocatalyst in water remediation
- PMID: 35518143
- PMCID: PMC9056492
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04512h
Novel MoS2 quantum dots as a highly efficient visible-light driven photocatalyst in water remediation
Abstract
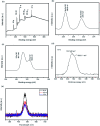
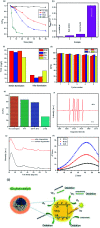
A direct and efficient hydrothermal system has been established for the synthesis of MoS2 quantum dots (QDs). Novel MoS2 QDs are an excellent potential photocatalysts to enhance photocatalytic response by charge separation under visible light irradiation. The optimum capability of QDs demonstrated the excellent photocatalytic ability for the degradation of organic pollutants. The microstructural, morphological, and optical properties of the MoS2 QDs are defined via X-ray diffraction (XRD), SEM, HRTEM, XPS, and UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy techniques. Under visible light irradiation, MoS2 QDs have great photocatalytic response for the degradation of Rh B that is 20 times higher than those of bulk MoS2 materials. The QDs possess practically the same catalytic response after 5 recycle runs, which is an evident proof of its stability. This course might pave the route toward creating current visible-light caused QD photocatalyst strategies for the highly valuable degradation of organic pollutants or antibiotics.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel fabrication of the recyclable MoS2/Bi2WO6 heterostructure and its effective photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under visible light irradiation.Chemosphere. 2022 Sep;303(Pt 1):134922. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134922. Epub 2022 May 11. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35568215
-
MoS2 quantum dots@TiO2 nanotube composites with enhanced photoexcited charge separation and high-efficiency visible-light driven photocatalysis.Nanotechnology. 2018 Mar 9;29(10):105403. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aaa68c. Nanotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29319002
-
The enhanced photocatalytic performance of SnS2@MoS2 QDs with highly-efficient charge transfer and visible light utilization for selective reduction of mythlen-blue.Nanotechnology. 2020 Nov 20;31(47):475602. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aba212. Nanotechnology. 2020. PMID: 32615552
-
Photocatalytic materials modified with carbon quantum dots for the degradation of organic pollutants under visible light: A review.Environ Res. 2022 Nov;214(Pt 4):114160. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114160. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 36027960 Review.
-
Sustainable hydrogen production for the greener environment by quantum dots-based efficient photocatalysts: A review.J Environ Manage. 2019 Oct 15;248:109246. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.07.017. Epub 2019 Jul 16. J Environ Manage. 2019. PMID: 31323456 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Role of MoS2 Quantum Dots in a Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reaction.ACS Org Inorg Au. 2022 Feb 22;2(3):205-213. doi: 10.1021/acsorginorgau.1c00040. eCollection 2022 Jun 1. ACS Org Inorg Au. 2022. PMID: 36855472 Free PMC article.
-
Molybdenum Disulfide-Based Catalysts in Organic Synthesis: State of the Art, Open Issues, and Future Perspectives.Small. 2024 Dec;20(52):e2406697. doi: 10.1002/smll.202406697. Epub 2024 Oct 20. Small. 2024. PMID: 39428828 Free PMC article.
-
Doped MoS2 Polymorph for an Improved Hydrogen Evolution Reaction.ACS Omega. 2023 Jul 13;8(29):26263-26275. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02623. eCollection 2023 Jul 25. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37521613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pálmai M. Zahran E. M. Angaramo S. Bálint S. Pászti Z. Knecht M. R. Bachas L. G. Pd-decorated m-BiVO4/BiOBr ternary composite with dual heterojunction for enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2017;5:529–534. doi: 10.1039/C6TA08357A. - DOI
-
- Dong S. Ding X. Guo T. Yue X. Han X. Sun J. Self-assembled hollow sphere shaped Bi2WO6/RGO composites for efficient sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;316:778–789. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.017. - DOI
-
- Dong S. Cui L. Liu C. Zhang F. Li K. Xia L. Su X. Feng J. Zhu Y. Sun J. Fabrication of 3D ultra-light graphene aerogel/Bi2 WO6 composite with excellent photocatalytic performance: A promising photocatalysts for water purification. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019;97:288–296. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2019.02.016. - DOI
-
- Wu D. Wang R. Yang C. An Y. Lu H. Wang H. Cao K. Gao Z. Zhang W. Xu F. Jiang K. Br doped porous bismuth oxychloride micro-sheets with rich oxygen vacancies and dominating {0 0 1} facets for enhanced nitrogen photo-fixation performances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019;556:111–119. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.08.048. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

