Fabrication of paper microfluidic devices using a toner laser printer
- PMID: 35518222
- PMCID: PMC9056319
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04301j
Fabrication of paper microfluidic devices using a toner laser printer
Abstract
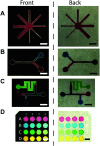
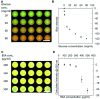
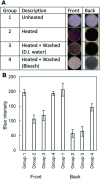
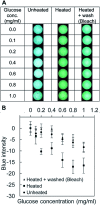
This paper describes a method to fabricate microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) using a toner laser printer. Multiple methods have been reported for the fabrication of μPADs for point-of-care diagnostics and environmental monitoring. Despite successful demonstrations, however, existing fabrication methods depend on particular printers, in-house instruments, and synthetic materials. In particular, recent discontinuation of the solid wax printer has made it difficult to fabricate μPADs with readily available instruments. Herein we reported the fabrication of μPADs using the most widely available type of printer: a toner laser printer. Heating of printed toner at 200 °C allowed the printed toner to reflow, and the spreading of the hydrophobic polymer through the filter paper was characterized. Using the developed μPADs, we conducted model colorimetric assays for glucose and bovine serum albumin (BSA). We found that heating of filter paper at 200 °C for 60 min caused the pyrolysis of cellulose in the paper. The pyrolysis resulted in the formation of aldehydes that could interfere with molecular assays involving redox reactions. To overcome this problem, we confirmed that the removal of the aldehyde could be readily achieved by washing the μPADs with aqueous bleach. Overall, the developed fabrication method should be compatible with most toner laser printers and will make μPADs accessible in resource-limited circumstances.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional toner for office laser printer and its application for printing of paper-based superwettable patterns and devices.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 3;13(1):12592. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39729-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37537193 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of laser printed microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (LP-µPADs) for point-of-care applications.Sci Rep. 2019 May 27;9(1):7896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44455-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31133720 Free PMC article.
-
Single step and mask-free 3D wax printing of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for glucose and nitrite assays.Talanta. 2019 Mar 1;194:837-845. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.10.104. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Talanta. 2019. PMID: 30609613
-
A review on wax printed microfluidic paper-based devices for international health.Biomicrofluidics. 2017 Aug 30;11(4):041501. doi: 10.1063/1.4991504. eCollection 2017 Jul. Biomicrofluidics. 2017. PMID: 28936274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensory materials for microfluidic paper based analytical devices - A review.Talanta. 2021 Dec 1;235:122733. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122733. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Talanta. 2021. PMID: 34517601 Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic paper analytic device (μPAD) technology for food safety applications.Biomicrofluidics. 2024 May 2;18(3):031501. doi: 10.1063/5.0192295. eCollection 2024 May. Biomicrofluidics. 2024. PMID: 38706979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments in Microfluidic Paper-based Analytical Devices for Pharmaceutical Analysis.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(27):2241-2260. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666221027144310. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36305123
-
3D-PAD: Paper-Based Analytical Devices with Integrated Three-Dimensional Features.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 17;11(3):84. doi: 10.3390/bios11030084. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802637 Free PMC article.
-
Paper-Based Biosensors for the Detection of Nucleic Acids from Pathogens.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 29;12(12):1094. doi: 10.3390/bios12121094. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A newly designed sticker-plastic sheet platform and smartphone-based digital imaging for protein assay in food samples with downscaling Kjeldahl digestion.RSC Adv. 2021 Nov 11;11(58):36494-36501. doi: 10.1039/d1ra04321h. eCollection 2021 Nov 10. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35494349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atabakhsh S. Jafarabadi Ashtiani S. Microfluid. Nanofluidics. 2019;23:69. doi: 10.1007/s10404-019-2233-y. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

