Carbon quantum dots and their biomedical and therapeutic applications: a review
- PMID: 35518468
- PMCID: PMC9061119
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra08088g
Carbon quantum dots and their biomedical and therapeutic applications: a review
Abstract
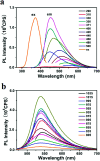
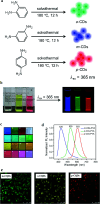
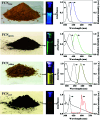
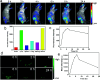
In recent years, nano carbon quantum dots (CQDs) have received increasing attention due to their properties such as small size, fluorescence emission, chemical stability, water solubility, easy synthesis, and the possibility of functionalization. CQDs are fluorescent 0D carbon nanostructures with sizes below 10 nm. The fluorescence in CQDs originates from two sources, the fluorescence emission from bandgap transitions of conjugated π-domains and fluorescence from surface defects. The CQDs can emit fluorescence in the near-infrared (NIR) spectral region which makes them appropriate for biomedical applications. The fluorescence in these structures can be tuned with respect to the excitation wavelength. The CQDs have found applications in different areas such as biomedicine, photocatalysis, photosensors, solar energy conversion, light emitting diodes (LEDs), etc. The biomedical applications of CQDs include bioimaging, drug delivery, gene delivery, and cancer therapy. The fluorescent CQDs have low toxicity and other exceptional physicochemical properties in comparison to heavy metals semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) which make them superior candidates for biomedical applications. In this review, the synthesis routes and optical properties of the CQDs are clarified and recent advances in CQDs biomedical applications in bioimaging (in vivo and in vitro), drug delivery, cancer therapy, their potential to pass blood-brain barrier (BBB), and gene delivery are discussed.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures








Similar articles
-
A review on nanostructured carbon quantum dots and their applications in biotechnology, sensors, and chemiluminescence.Talanta. 2019 May 1;196:456-478. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.12.042. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Talanta. 2019. PMID: 30683392 Review.
-
Organosilane-functionalized carbon quantum dots and their applications to "on-off-on" fluorometric determination of chromate and ascorbic acid, and in white light-emitting devices.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Jul 6;186(8):516. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3603-6. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31280375
-
Carbon quantum dots in bioimaging and biomedicines.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 22;11:1333752. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1333752. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38318419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon quantum dots: An approach in cancer theranostics.Biomater Adv. 2022 May;136:212756. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2022.212756. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Biomater Adv. 2022. PMID: 35929302 Review.
-
Scalable synthesis of organic-soluble carbon quantum dots: superior optical properties in solvents, solids, and LEDs.Nanoscale. 2017 Sep 14;9(35):13195-13202. doi: 10.1039/c7nr04718e. Nanoscale. 2017. PMID: 28853478
Cited by
-
Learning from Nature: Bioinspired Chlorin-Based Photosensitizers Immobilized on Carbon Materials for Combined Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy.Biomimetics (Basel). 2020 Oct 14;5(4):53. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics5040053. Biomimetics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon-Based Nanostructures as Emerging Materials for Gene Delivery Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 18;16(2):288. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020288. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of green fluorescent nano-sensors for the determination of furosemide in biological samples and pharmaceutical preparations.BMC Chem. 2023 Mar 24;17(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13065-023-00937-y. BMC Chem. 2023. PMID: 36964587 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of Quantum Dots and Their Therapeutic Applications in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer and SARS-CoV-2.Adv Pharm Bull. 2023 Jul;13(3):411-422. doi: 10.34172/apb.2023.065. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Adv Pharm Bull. 2023. PMID: 37646053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Covalent and Noncovalent Loading of Doxorubicin by Folic Acid-Carbon Dot Nanoparticles for Cancer Theranostics.ACS Omega. 2022 Jun 24;7(27):23322-23331. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01482. eCollection 2022 Jul 12. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35847251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luo P. G. et al., Carbon-based quantum dots for fluorescence imaging of cells and tissues. RSC Adv. 2014;4(21):10791–10807. doi: 10.1039/C3RA47683A. - DOI
-
- Yuan F. et al., Shining carbon dots: synthesis and biomedical and optoelectronic applications. Nano Today. 2016;11(5):565–586. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2016.08.006. - DOI
-
- Mirtchev P. et al., Solution phase synthesis of carbon quantum dots as sensitizers for nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012;22(4):1265–1269. doi: 10.1039/C1JM14112K. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

