Fungal community analysis in seawater of the Mariana Trench as estimated by Illumina HiSeq
- PMID: 35518513
- PMCID: PMC9061085
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra10142f
Fungal community analysis in seawater of the Mariana Trench as estimated by Illumina HiSeq
Abstract
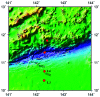
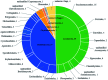
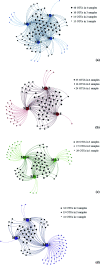
This study assessed the diversity and distribution of fungal communities in thirteen marine seawater samples from four sites (L1, L3, L4 and L7) of the Mariana Trench, with a depth range of 1000-4000 meters, using Illumine Hiseq sequencing with fungal-specific primers targeting the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region of the ribosomal rRNA gene. Sedimentary fungal communities showed high diversity with 209 880 reads belonging to 91 operational taxonomic units (OTUs). Of these OTUs, 45 belonged to the Ascomycota, 37 to Basidiomycota, 3 to Chytridiomycota, 1 to Glomeromycota, 1 to Cryptomycota, and 4 to unknown fungi. The major fungal orders included Saccharomycetales and Sporidiobolales. The commonly found fungal genera were Candida, Malassezia and Cryptococcus. These results suggest the existence of diverse fungal communities in the Mariana Trench marine seawater, which can be considered as a useful community model for further ecological and evolutionary study of fungi in the trench.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pabba S. K. Samatha B. Prasad M. R. Nidadavolu S. H. Charya M. A. S. Antibacterial Activity of Marine derived Fungi Collected from South East Coast of Tamilnadu, India. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Res. 2017;1:86–89.
-
- Liberra K. Lindequist U. Marine fungi--a prolific resource of biologically active natural products? Die Pharmazie. 1995;50:583–588. - PubMed
-
- Jones E. B. G. Sakayaroj J. Suetrong S. Somrithipol S. Pang K. Classification of marine Ascomycota, anamorphic taxa and Basidiomycota. Fungal Divers. 2009;35:1–187.
-
- Hyde K. D. Jones E. B. G. Leano E. M. Pointing S. B. Poonyth A. D. Vrijmoed L. L. P. Role of fungi in marine ecosystems. Biodiversity & Conservation. 1998;7:1147–1161.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

