Canonical Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Regulates Expression of Aquaporin-4 and Its Anchoring Complex in Mouse Astrocytes
- PMID: 35518645
- PMCID: PMC9067306
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.878154
Canonical Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Regulates Expression of Aquaporin-4 and Its Anchoring Complex in Mouse Astrocytes
Abstract
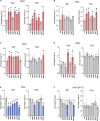
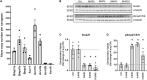
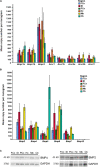
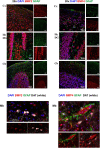
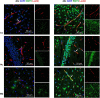
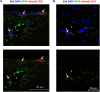
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is the predominant water channel in the brain; it is enriched in astrocytic foot processes abutting vessels where it is anchored through an interaction with the dystrophin-associated protein (DAP) complex. Enhanced expression with concomitant mislocalization of AQP4 along astrocyte plasma membranes is a hallmark of several neurological conditions. Thus, there is an urgent need to identify which signaling pathways dictate AQP4 microdistribution. Here we show that canonical bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), particularly BMP2 and 4, upregulate AQP4 expression in astrocytes and dysregulate the associated DAP complex by differentially affecting its individual members. We further demonstrate the presence of BMP receptors and Smad1/5/9 pathway activation in BMP treated astrocytes. Our analysis of adult mouse brain reveals BMP2 and 4 in neurons and in a subclass of endothelial cells and activated Smad1/5/9 in astrocytes. We conclude that the canonical BMP-signaling pathway might be responsible for regulating the expression of AQP4 and of DAP complex proteins that govern the subcellular compartmentation of this aquaporin.
Keywords: Smad1/5/9; aquaporin-4; astrocyte; bone morphogenetic protein; dystrophin.
Copyright © 2022 Skauli, Savchenko, Ottersen, Roybon and Amiry-Moghaddam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M., Xue R., Haug F. M., Neely J. D., Bhardwaj A., Agre P., et al. (2004b). Alpha-syntrophin deletion removes the perivascular but not endothelial pool of aquaporin-4 at the blood-brain barrier and delays the development of brain edema in an experimental model of acute hyponatremia. Faseb J. 18 542–544. 10.1096/fj.03-0869fje - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M., Williamson A., Palomba M., Eid T., de Lanerolle N. C., Nagelhus E. A., et al. (2003b). Delayed K+ clearance associated with aquaporin-4 mislocalization: phenotypic defects in brains of alpha-syntrophin-null mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 13615–13620. 10.1073/pnas.2336064100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M., Otsuka T., Hurn P. D., Traystman R. J., Haug F. M., Froehner S. C., et al. (2003a). An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 2106–2111. 10.1073/pnas.0437946100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

