A pH tuning single fluorescent probe based on naphthalene for dual-analytes (Mg2+ and Al3+) and its application in cell imaging
- PMID: 35518728
- PMCID: PMC9054541
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra02101f
A pH tuning single fluorescent probe based on naphthalene for dual-analytes (Mg2+ and Al3+) and its application in cell imaging
Abstract
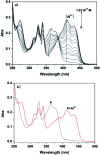
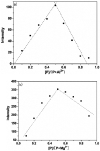
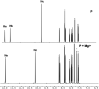
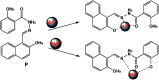
In this study, a naphthalene Schiff-base P which serves as a dual-analyte probe for the quantitative detection of Al3+ and Mg2+ has been designed. The proposed probe showed an ''off-on'' fluorescent response toward Al3+ in ethanol-water solution (1 : 9, v/v, pH 6.3, 20 mM HEPES) over other metal ions and anions, while the detection by the probe could be switched to Mg2+ by regulating the pH from 6.3 to 9.4. The sensing mechanisms of P to Al3+/Mg2+ are attributed to inhibition of the photo-induced electron transfer (PET) process by the formation of 1 : 1 ligand-metal complexes. More importantly, the probe was applied successfully in living cells for the fluorescent cell-imaging of Al3+ and Mg2+.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures






References
-
- Liu Z. C. Yang Z. Y. Li Y. X. Li T. R. Wang B. D. Li Y. Jin X. L. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2013;395:77. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2012.10.009. - DOI
- Qin J. C. Fan L. Li T. R. Yang Z. Y. Synth. Met. 2015;199:179. doi: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2014.11.030. - DOI
- Barceló J. Poschenrieder C. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2002;48:75. doi: 10.1016/S0098-8472(02)00013-8. - DOI
- King S. W. Savory J. Willis M. R. Gitelman H. J. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1981;14:1. doi: 10.3109/10408368109105861. - DOI - PubMed
- Parkinson I. S. Ward M. K. Kerr D. N. J. Clin. Pathol. 1981;34:1285. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.11.1285. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Zhou J. Horev B. Hwang G. Klein M. I. Koo H. Benoit D. S. J. Mater. Chem. 2016;4:3075. doi: 10.1039/C5TB02054A. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Fu Y. L. Tu Y. Y. Fan C. B. Zheng C. H. Liu G. Pu S. Z. New J. Chem. 2016;40:8579. doi: 10.1039/C6NJ01458E. - DOI
- Pu S. Z. Zhang C. C. Fan C. B. Liu G. Dyes Pigm. 2016;129:24. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.02.001. - DOI
- Ding H. C. Li B. Q. Pu S. Z. Liu G. Jia D. C. Yu Z. Sens. Actuators, B. 2017;247:26. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.02.172. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

