Pasireotide for Refractory Hypoglycemia in Malignant Insulinoma- Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 35518928
- PMCID: PMC9063459
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.860614
Pasireotide for Refractory Hypoglycemia in Malignant Insulinoma- Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
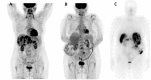
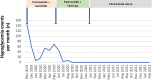
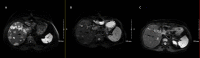
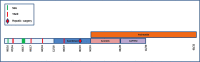
Malignant insulinomas are functional neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas and the primary cause of tumor-related hypoglycemia. Malignant insulinoma is rare and has a poor prognosis. We report a case of metastatic malignant insulinoma in a 64-year-old female patient with severe and refractory hypoglycemia. After several ineffective locoregional and systemic therapeutic lines for the secretory disease, the introduction of pasireotide, a second-generation somatostatin analog, provided an improved clinical and secretory evolution both quickly and sustainably, with an excellent safety profile. Pasireotide is an effective and well-tolerated therapy in the treatment of refractory hypoglycemia in metastatic insulinoma.
Keywords: malignant insulinoma; neuroendocrine tumor; pancreatic neuroendocrine cancer; pasireotide; refractory hypoglycemia.
Copyright © 2022 Oziel-Taieb, Maniry-Quellier, Chanez, Poizat, Ewald and Niccoli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- de Herder WW, Zandee WT, Hofland J. Insulinoma - Diffuse Hormonal Systems and Neuroendocrine Tumor Syndromes. In Comprehensive Endocrinology Book (2000).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

