Recent advances and future perspectives of sol-gel derived porous bioactive glasses: a review
- PMID: 35519068
- PMCID: PMC9056785
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04287k
Recent advances and future perspectives of sol-gel derived porous bioactive glasses: a review
Abstract
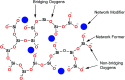
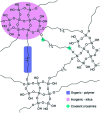
The sol-gel derived porous bioactive glasses have drawn worldwide attention by virtue of the convenience and flexibility of this versatile synthesis method. In this review, the recent advances in sol-gel processed porous bioactive glasses in biomedical fields, especially for bone tissue regeneration applications have been comprehensively reviewed. Generally, it is envisaged that the morphology and chemical compositions of sol-gel derived porous bioactive glasses significantly affect their biological properties. Therefore, the controlled synthesis of these porous glasses is critical to their effective use in the biomedical fields. With this context, the first part of the review briefly describes the fundamentals of the sol-gel technique. In the subsequent section, different approaches frequently used for the sol-gel synthesis of porous glasses such as microemulsion and acid-catalyzed based synthesis have been reviewed. In the later part of the review, different types of sol-gel derived bioactive glasses namely silica, phosphate and silica-titania based glasses along with organic-inorganic hybrids materials have been discussed. The review also discusses the chemical, surface, mechanical and biological properties and further highlights the strategies to control the pore structure, shape, size and compositions of sol-gel derived bioactive glasses. Finally, the review provides a detailed discussion about the bone tissue regeneration application of different types of sol-gel derived bioactive glasses and presents future research perspectives.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- Owens G. J. Singh R. K. Foroutan F. Alqaysi M. Han C. M. Mahapatra C. Kim H. W. Sol–gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016;77:1–79. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.12.001. - DOI
-
- Tan S. N. Wang W. Ge L. 3.30 Biosensors based on sol–gel derived materials. Compr. Biomater. II. 2017;3:657–689.
-
- Monton M. R. N. Forsberg E. M. Brennan J. D. Tailoring sol–gel derived silica materials for optical biosensing. Chem. Mater. 2012;24:796–811. doi: 10.1021/cm202798e. - DOI
-
- Akpan U. G. Hameed B. H. The advancement in sol–gel method of doped TiO2 photocatalyst. Appl. Catal., A. 2010;375:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.12.023. - DOI
-
- Levy D. and Zayat M., The sol–gel handbook, ed. D. Levy and M. Zayat, vol. 1–3, Wiley VCH, USA, 2015, pp. 1–1508
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

