Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/poly(amine)-coated nickel oxide nanoparticles for norfloxacin delivery: antibacterial and cytotoxicity efficiency
- PMID: 35519075
- PMCID: PMC9056780
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04784h
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/poly(amine)-coated nickel oxide nanoparticles for norfloxacin delivery: antibacterial and cytotoxicity efficiency
Abstract
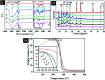
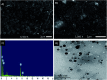
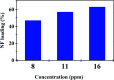
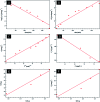
Sustained release dosage forms enable prolonged and continuous release of a drug in the gastrointestinal tract for medication characterized by a short half lifetime. In this study, the effect of blending polyamine on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) as a carrier for norfloxacin (NF) was studied. The prepared blend was mixed with different amounts of NiO nanoparticles and characterized using FTIR analysis, X-ray diffraction analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, dynamic light scattering, transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. It was found that the drug released from the nanocomposite has a slow rate in comparison with NiO, PHB, and PHB/polyamine blend. The highest ratio of NiO content to the matrix (highest NF loading), leads to a slower rate of drug release. The release from the nanocomposites showed a faster rate at pH = 2 than that at pH = 7.4. The mechanisms of NF adsorption and release were studied on PHB/polyamine-3% NiO nanocomposite. In addition, the antimicrobial efficacy of nanocomposites loaded with the drug was determined and compared with the free drug. Inclusion of NiO into PHB/polyamine showed a higher efficacy against Streptococcus pyogenes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa than the free NF. Moreover, the cytotoxicity of PHB/polyamine-3% NiO against HePG-2 cells was investigated and compared with PHB and PHB/polyamine loaded with the drug. The most efficient IC50 was found for NF@PHB/polyamine-3% NiO (29.67 μg mL-1). No effect on cell proliferation against the normal human cell line (WISH) was observed and IC50 was detected to be 44.95 and 70 μg mL-1 for NiO nanoparticles and the PHB/polyamine-3% NiO nanocomposite, respectively indicating a selectivity of action towards tumor cells coupled with a lack of cytotoxicity towards normal cells.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/polyethylene glycol-NiO nanocomposite for NOR delivery: Antibacterial activity and cytotoxic effect against cancer cell lines.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Jul 15;114:717-727. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.050. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29548916
-
Preparation, characterization and evaluation of antibacterial properties of epirubicin loaded PHB and PHBV nanoparticles.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Feb 1;144:259-266. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.049. Epub 2019 Dec 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 31821825
-
Bioresponsive gingerol-loaded alginate-coated niosomal nanoparticles for targeting intracellular bacteria and cancer cells.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Feb;258(Pt 2):128957. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128957. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38154726
-
Photocatalysis and adsorption kinetics of azo dyes by nanoparticles of nickel oxide and copper oxide and their nanocomposite in an aqueous medium.PeerJ. 2022 Nov 14;10:e14358. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14358. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36405015 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the nano-level molecular packing in chitosan-NiO nanocomposite by using positron annihilation spectroscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering.Chemphyschem. 2013 Apr 2;14(5):1055-62. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201200902. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Chemphyschem. 2013. PMID: 23418038
Cited by
-
The Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and PHA-Based Nanoparticles.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 27;13(19):3302. doi: 10.3390/polym13193302. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34641118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH-driven enhancement of anti-tubercular drug loading on iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery in macrophages.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2021 Oct 7;12:1127-1139. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.12.84. eCollection 2021. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34703723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lokesh K. Kavitha G. Manikandan E. Mani G. K. Kaviyarasu K. Rayappan J. B. B. Ladchumananandasivam R. Aanand J. S. Jayachandran M. Maaza M. IEEE Sens. J. 2016;16:2477–2483.
-
- Manikandan E. Kennedy J. Kavitha G. Kaviyarasu K. Maaza M. Panigrahi B. Mudali U. K. J. Alloys Compd. 2015;647:141–145. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.06.102. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

