Next-generation of selective histone deacetylase inhibitors
- PMID: 35519364
- PMCID: PMC9065321
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra02985k
Next-generation of selective histone deacetylase inhibitors
Abstract
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are clinically validated epigenetic drug targets for cancer treatment. HDACs inhibitors (HDACis) have been successfully applied against a series of cancers. First-generation inhibitors are mainly pan-HDACis that target multiple isoforms which might lead to serious side effects. At present, the next-generation HDACis are mainly focused on being class- or isoform-selective which can provide improved risk-benefit profiles compared to non-selective inhibitors. Because of the rapid development in next-generation HDACis, it is necessary to have an updated and state-of-the-art overview. Here, we summarize the strategies and achievements of the selective HDACis.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

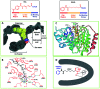
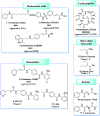
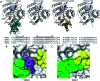
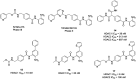
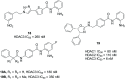
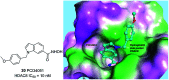
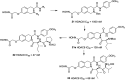
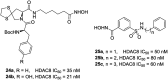
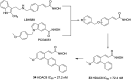
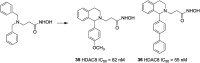
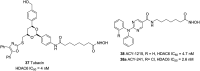
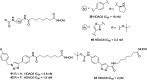
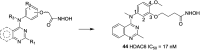
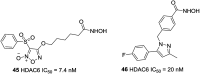
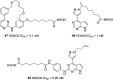
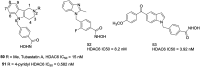
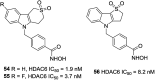
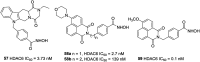
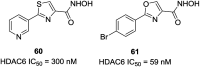
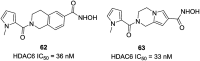
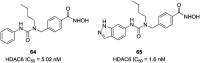
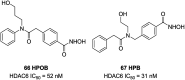
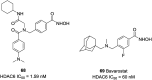
References
-
- Damaskos C. Tomos I. Garmpis N. Karakatsani A. Dimitroulis D. Garmpi A. Spartalis E. Kampolis C. F. Tsagkari E. Loukeri A. A. Margonis G.-A. Spartalis M. Andreatos N. Schizas D. Kokkineli S. Antoniou E. A. Nonni A. Tsourouflis G. Markatos K. Kontzoglou K. Kostakis A. Tomos P. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:37–43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

